“Investing in your mental health is worthwhile. Put yourself first, get help if you need it, and watch yourself get better.” – Wellness Kraft
Table of Contents
Introduction
Mental health is an important part of general health, and being able to recognize the signs of a mental health crisis is key to getting help and help on time. Individuals who are going through a mental health crisis may undergo significant changes in their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that can affect how well they live and how well they work. We can help individuals get through these difficult times and find the help they need by understanding the warning signs and taking the right steps. In this piece, we’ll talk about the warning signs of a mental health crisis, the most important things to remember, and common questions to help raise awareness and understanding.
The Four Phases of Mental Health Crisis
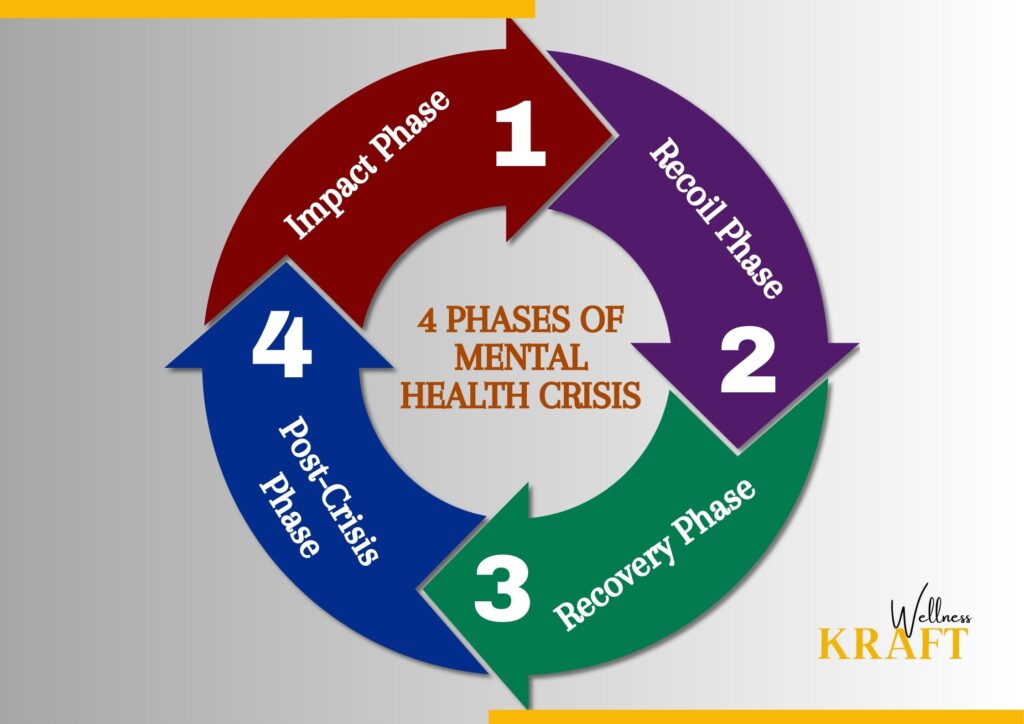
1) Impact Phase:
The first stage of a mental health crisis is the impact phase. It is caused by a stressful event or stressor that overwhelms a person’s ability to deal with it in a healthy way. The person may experience a variety of strong feelings, as well as confusion, shock, and disorientation, during this phase.
2) Recoil Phase:
The next step is the “recoil” phase, which happens after the initial impact and includes both emotional and mental reactions. As people start to deal with the crisis, they may show signs of denial, anger, sadness, or worry. During this phase, people try to get back to a sense of stability and control.
3) Recovery Phase:
After a crisis, the focus of the recovery phase is on adjusting and rebuilding. People slowly get back to being able to work and deal with the problems they face. In order to manage their feelings and deal with the fallout from the crisis, they may seek support, engage in therapy, and develop coping mechanisms.
4) Post-Crisis Phase:
The long-term effects of the mental health crisis can be seen in the “post-crisis” phase. Individuals may still experience lingering effects even though the crisis’ intensity may have lessened. During this phase, you put the lessons you’ve learned from the crisis to use, adjust to changes, and work on your own growth and resiliency.
It’s important to remember that the length of these phases and how quickly they pass can vary a lot depending on the person and the type of crisis. Not everyone who experiences a crisis goes through all four phases, and some individuals may need support and treatment even after the crisis is over.
In order to support the recovery and well-being of individuals going through a mental health crisis, it is crucial to seek the right expert help https://www.crisistextline.org/ , rely on a support system, and engage in self-care practices during each phase.
Warning Signs of Mental Health Crisis

Each person’s warning signs of a mental health crisis can look different, but here are some common ones to look out for:
1) Sudden and Significant Changes in Behavior:
Sudden and significant changes in behavior, like greater anger, aggression, or withdrawal from social activities.Changes in mood or behavior that are sudden and noticeable, such as long-lasting sadness, irritability, anger, or mood swings that are too extreme. Changes in behavior may include engaging in risky activities, social withdrawal, or losing interest in previously enjoyed activities.
2) Emotional Instability:
Emotional instability means having strong and powerful feelings, such as frequent outbursts of anger, sadness, irritability, or an inability to feel emotions. Intense emotional distress is a feeling of hopelessness, helplessness, sorrow, or not being worth anything. Feelings of worry, fear, or panic that don’t go away and get in the way of daily life.
3) Social Isolation:
Social Isolation is the withdrawal from social interactions, the separation from friends, family, and daily activities. Avoiding social interactions and pulling away from friends, family, and activities you used to enjoy. A feeling of being separate from others or a sense of being cut off from them.
4) Disturbed Sleep Patterns:
Significant changes in sleep patterns, such as insomnia (having trouble sleeping) or hypersomnia (being too sleepy). Significant changes in sleep habits like insomnia (difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep), hypersomnia (excessive sleepiness), or recurring nightmares.
5) Difficulty in Concentrating:
Problems with focus, memory, making decisions, or being unable to finish jobs are signs of having trouble concentrating. Trouble focusing, making decisions, or experiencing erratic thoughts. Memory problems or trouble thinking clearly and rationally. Cognitive distortions are persistent bad thoughts, wrong ways of thinking, or too much worry that make it hard to get through the day and give one a sense of hopelessness.
6) Extreme Changes in Energy Levels:
Having sudden and prolonged bouts of tiredness or restlessness, as well as other significant changes in energy levels. Physical symptoms are problems with your body that you can’t explain, like headaches, stomachaches, tight muscles, or changes in your appetite and weight. Lack of energy or feeling tired all the time.
7) Neglecting Personal Care:
Ignoring personal hygiene, appearance, or previously important activities. There is a big drop in personal cleanliness, people stop taking care of themselves, and they lose interest in how they look or how they groom themselves.
8) Changes in Appetite or Weight:
Big changes in appetite or weight, like an increase or decrease in food intake that is obvious. Individuals experiencing a mental health crisis may experience significant changes in weight or appetite. These changes can show as increased or decreased appetite and weight gain or reduction. The relationship between mental health and appetite and weight is complex.
9) Substance Abuse:
Substance abuse is when someone uses booze, drugs, or other substances more and more as a way to deal with problems. Use of drugs is getting worse and it’s hard to stop or control it.
10) Expressing Hopelessness or Suicidal Thoughts:
Saying out loud that you feel hopeless or useless, or that you are having suicidal thoughts. https://suicidepreventionlifeline.org/chat/ Having thoughts of suicide, self-harm, or engaging in self-destructive behavior. These signs should be taken seriously, and help should be found as soon as possible.
It’s important to remember that these signs may point to a possible mental health crisis, but in order to get an exact diagnosis, a professional evaluation by a qualified healthcare provider is needed. If you or someone you know shows these warning signs, it is important to support them to get help right away from a mental health professional https://988lifeline.org/ , a counselor, or a helpline in their country.
Strategies For Overcoming The Signs of a Mental Health Crisis

1) Sudden and Significant Changes in Behavior:
-Seek professional help from a mental health specialist who can assess your issue and prescribe therapy or medication.
-Engage in stress-relieving activities like mindfulness, deep breathing, and relaxation techniques.
-Build a support system of reliable friends and family who can offer understanding and help during challenging times.
2) Emotional Instability:
-Engage in self-care activities that improve emotional well-being, such as hobbies, outdoors, or relaxation techniques.
-To learn coping and emotional control skills, try CBT or DBT.
-Contact emotional crisis support groups or helplines. https://www.veteranscrisisline.net/
3) Social Isolation:
-To find social connection and support, turn to trusted friends, family, or support groups.
-Enjoy enjoyable social activities and hobbies.
-Consider therapy or counseling to address the causes of social separation and discover healthy strategies to reconnect.
4) Disturbed Sleep Patterns:
-Set a regular bedtime and wake time.
-Take a warm bath, read, or practice relaxation before bed.
-Avoid caffeine and electronics before bed to avoid sleep disruption.
5) Difficulty in Concentrating:
-To concentrate, break things into smaller steps. -Meditation can increase cognitive clarity and minimize racing thoughts.-Consider obtaining mental health support from a professional who can help improve cognitive function.
6) Extreme Changes in Energy Levels:
-Consult a health care practitioner to rule out medical issues. -Exercise can help relieve stress and promote well-being. -Stress management techniques including deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and yoga can reduce physical symptoms.
7) Neglecting Personal Care:
-Maintaining cleanliness, eating well, and exercising are self-care activities. -Recognizing your value and emphasizing your well-being is self-compassion. -Seek support from a mental health professional who can help with underlying issues causing self-neglect.
8) Changes in Appetite or Weight:
-Focus on getting therapy or counseling to deal with any underlying mental health problems. -Pay attention to your hunger and fullness signals when you eat mindfully. -With the help of a trained dietitian or nutritionist, make a balanced meal plan to make sure you’re getting enough nutrition and to fix any problems.
9) Substance Abuse:
-Through counseling, therapy, or support groups specializing in addiction treatment, seek professional help.
-To lessen your need for substances, look into healthier coping strategies and stress management techniques.
-Exercise, hobbies, and developing a supportive social network are all examples of activities that support a healthy lifestyle.
10) Expressing Hopelessness or Suicidal Thoughts:
-If you or a loved one is experiencing suicidal thoughts, call a helpline or 911. -To receive crisis assistance and ongoing support, contact a mental health professional. -Create a safety plan with a mental health specialist, including support networks and coping strategies.
Research Analysis
So, here are some of the most significant findings and concepts that have come out of research on the mental health crisis:
Global Burden:
One in four people will experience a mental health condition at some point in their lives, according to estimates from the World Health Organization (WHO). Mental health disorders add significantly to the global burden of disease.
Socioeconomic Factors: (Patel et al., 2018) Research shows that socioeconomic factors like poverty, unemployment, and differences in income are linked to higher rates of mental health problems.
Stigma and Barriers to Care:
The stigma associated with mental health is still a significant deterrent to seeking help. Research (Clement et al., 2015) shows how important it is to lessen stigma and make it easier to get mental health care.
Risk Factors:
Genetic predisposition, adverse childhood experiences (ACEs), trauma, drug abuse, and social isolation are all risk factors that can lead to mental health problems (Kessler et al., 2010; McLaughlin et al., 2012).
Impact on Productivity and Well-Being:
(Hilton et al., 2008; Harvey et al., 2017) Mental health problems have a big impact on how productive people are, how often they miss work, and how happy they are overall.
Treatment and Support:
Research shows that evidence-based treatments like therapy (e.g., cognitive-behavioral therapy, dialectical behavior therapy) and medication are helpful in managing mental health conditions (National Institute of Mental Health, n.d. )
Major Countries Facing Mental health Crisis
Due to a number of different factors, the prevalence of mental health conditions varies between countries. While it’s important to remember that mental health challenges occur everywhere, some countries are more affected by particular conditions. Here are just a few:
United States:
Due to factors like high stress levels, social pressures, easy access to firearms, and a fragmented mental health care system, the United States has a high prevalence of mental health conditions. The prevalence of mental health challenges can also be influenced by cultural factors like individualism and the stigma that surrounds mental health.
India:
Due to a number of factors, India has a significant burden of mental health conditions. Rapid urbanization, cultural norms, poverty, limited access to mental health services, and the stigma surrounding mental health all add to the high prevalence. Indian society’s diversity and complexity can also have an impact on mental health.
United Kingdom:
Mental health problems are common in the UK. This is partly due to factors like work-related stress, economic stresses, and seasonal affective disorder (SAD), which is caused by the lack of sunlight in the winter. Despite attempts to improve mental health services in the UK, there are still challenges like long wait times and differences in access to care.
Australia:
The prevalence of mental health conditions is high in Australia. This can be traced to factors like the high rate of drug abuse, the isolation of some areas, the high rates of depression and anxiety, and the impact of past trauma on indigenous communities. The country has taken steps to deal with mental health problems, such as running campaigns to raise understanding and giving more money to mental health services.
Japan:
Mental health challenges are becoming more prevalent in Japan. Some of the things that contribute to this are a demanding work culture, social stresses, high suicide rates, and the social stigma of getting help for mental health problems. The Japanese government has taken steps to improve access to mental health care services after recognizing the need to address mental health.
It’s important to remember that the social, cultural, economic, and historical factors that affect mental health challenges in each country are complex and can change over time. No country is immune to the impact of mental health challenges, which are present worldwide. Promoting awareness, reducing stigma, and making sure everyone has access to good mental health care are all important ways to deal with mental health conditions around the world.
Key Takeaways
1) Recognizing mental health crisis warning signs is essential for early intervention and support. Prompt action can help prevent symptoms from worsening.
2) In a mental health crisis, professional examination by a skilled mental health clinician is crucial for accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and continuous support.
3) Building a solid support system of trustworthy individuals, such as friends, family, or support groups, is key to offering understanding, encouragement, and aid during a mental health crisis.
4) During a mental health crisis, self-care activities, stress management techniques, and coping skills can help manage symptoms and promote wellbeing.
5) Raising awareness and understanding of mental health difficulties, particularly crisis warning signs, can help minimize stigma, encourage early intervention, and create a more supportive atmosphere for individuals in need.
Concluding Thoughts
In conclusion, supporting individuals in need and promoting overall well-being depend on understanding and addressing mental health crises. To get through these tough scenarios, it’s important to recognize the warning signs, get professional help, and create a supportive environment.
Individuals’ emotions, thoughts, behaviors, and general functioning can all be impacted by mental health crises, as stated in the Wellness Kraft article. We can help reduce stigma and create a more caring society that supports those experiencing mental health crises by raising awareness and information about these issues.
FAQs
1) What makes a mental health crisis different from normal stress or sadness?
A mental health crisis is characterized by severe and disruptive symptoms that greatly impair daily functioning, whereas normal stress or sadness is typically transient and manageable.
2) How can I provide support for someone who is experiencing a mental health crisis?
Provide a nonjudgmental mental listening ear, encourage professional support seeking, and help create a supportive atmosphere. Be patient and understanding while validating their experiences.
3) Are individuals more likely to experience a mental health crisis if they have certain risk factors?
Yes, things like a history of mental illness in the family, past trauma, chronic stress, drug use, and certain life events can make someone more likely to have a mental health crisis.
4) What should I do if I or someone I know is showing warning signs of a mental health crisis?
Talk to a mental health provider, a counselor, or a helpline to get professional help. Share your worries with individuals you can trust, and push them to talk openly about their feelings and experiences.
5) How do I tell the difference between normal ups and downs in my mood and a mental health crisis?
A mental health crisis is characterized by more severe and persistent symptoms that may significantly impair functioning and interfere with daily life and may call for professional intervention.
6) Can you treat mental health crises?
Yes, most mental health crises can be helped. Individuals can experience relief from symptoms and work toward recovery with the right evaluation, treatment, and support.
7) What are some self-care activities that can help in a mental health crisis?
Promoting mental well-being can be done by engaging in activities like exercise, mindfulness or meditation, keeping a balanced schedule, pursuing hobbies, spending time with loved ones, and putting self-care first.
8) Without professional intervention, can a mental health crisis get better?
Answer: Professional intervention is advised for accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and ongoing support during a mental health crisis, even though some individuals may experience temporary relief.
9) On average, how long does a mental health crisis last?
From person to person, the duration of a mental health crisis changes. The process of intervention and recovery is influenced by a number of factors, including timing, intensity, and duration.
10) For individuals experiencing a mental health crisis, where can I find resources and support?
Mental health groups, help lines, online platforms, and healthcare providers are all good places to look for resources. They give people knowledge, access to support networks, and help from professionals.