“Air pollution is a complex problem with no easy solution. But with determination and collaboration, we can make a difference and create a cleaner, healthier world.” – Wellness Kraft
Introduction
Around the world, air pollution is a developing problem that has a negative impact on both human health and the environment. Women are a particularly vulnerable population to the harmful impacts, with numerous studies showing that they are at a higher risk of experiencing negative health effects compared to men.
This is due to a combination of factors, including biological differences, social and cultural norms, and differences in exposure to pollution sources. In this article, we will explore the effects of air pollution on women’s health, focusing on respiratory, reproductive, cardiovascular, and mental health outcomes. We will also examine the concept of environmental justice and how it relates to women’s health, as well as ways to mitigate and prevent air pollution.
Table of Contents
Why Women’s Health is Specifically Impacted
Women are disproportionately impacted by air pollution due to a variety of factors.
Firstly, women’s lungs are smaller than men’s on average, meaning that they breathe in a greater amount of air relative to their lung size. This increases the likelihood of harmful pollutants entering the bloodstream and causing damage. Additionally, women tend to have higher levels of body fat than men, which can act as a reservoir for certain pollutants.
Social and cultural norms also play a role in women’s increased vulnerability to air pollution. Women are more likely to work in indoor environments, such as factories and offices, which can expose them to higher levels of indoor air pollution. Women also tend to take on a greater burden of household chores, such as cooking and cleaning, which can expose them to pollutants emitted from household products and appliances.
Women from disadvantaged communities are often exposed to higher levels of outdoor pollution due to factors such as living near industrial facilities and highways. These communities may also lack access to healthcare and other resources to mitigate the effects of air pollution.
Taken together, these factors contribute to women’s increased susceptibility to the negative health effects of air pollution.
Respiratory Health Effects

-Increased risk of asthma
-Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
-Lung cancer
Exposure to air pollution has been linked to a range of respiratory health problems for women. One of the most well-established associations is with an increased risk of asthma. A number of studies have found that women who live in areas with high levels of pollution are more likely to develop asthma or experience worsening of existing asthma symptoms.
It has also been linked to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a progressive lung disease that makes it difficult to breathe. Women who are exposed to high levels of pollution are at greater risk of developing COPD, and studies have shown that they experience more severe symptoms compared to men.
Exposure has been linked to an increased risk of lung cancer in women. This may be due to the fact that women’s lungs are more susceptible to damage from pollutants, or to the fact that they may be exposed to pollutants through a greater variety of sources, such as cooking indoors with solid fuels.
Reproductive Health Effects
-Infertility
-complications
-Low birth weight
In addition to respiratory health effects, air pollution can also have significant reproductive health effects on women. Exposure has been linked to infertility, pregnancy complications, and low birth weight.
Infertility is a common issue that affects many women and their partners. Studies have shown that exposure to air pollution, particularly PM2.5 and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), can decrease fertility rates in women. These pollutants can also cause damage to reproductive organs and DNA, which can further impact fertility.
Pregnancy complications, such as gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, and gestational diabetes, have also been linked to exposure to air pollution. Women who are exposed to higher levels of pollution during pregnancy are at a greater risk of developing these complications, which can have long-lasting impacts on maternal and fetal health.
Exposure has been linked to low birth weight in newborns. Low birth weight can have significant health consequences for infants, including an increased risk of respiratory issues, developmental delays, and chronic health conditions later in life.
According to studies, pregnant women who are exposed to PM2.5 and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) are at an increased risk of having babies that are underweight.
Overall, the reproductive health effects on women are significant and can have long-lasting consequences on maternal and fetal health. It is important for individuals, policymakers, and industries to take steps to reduce air pollution and mitigate its negative impacts on reproductive health.
Cardiovascular Health Effects
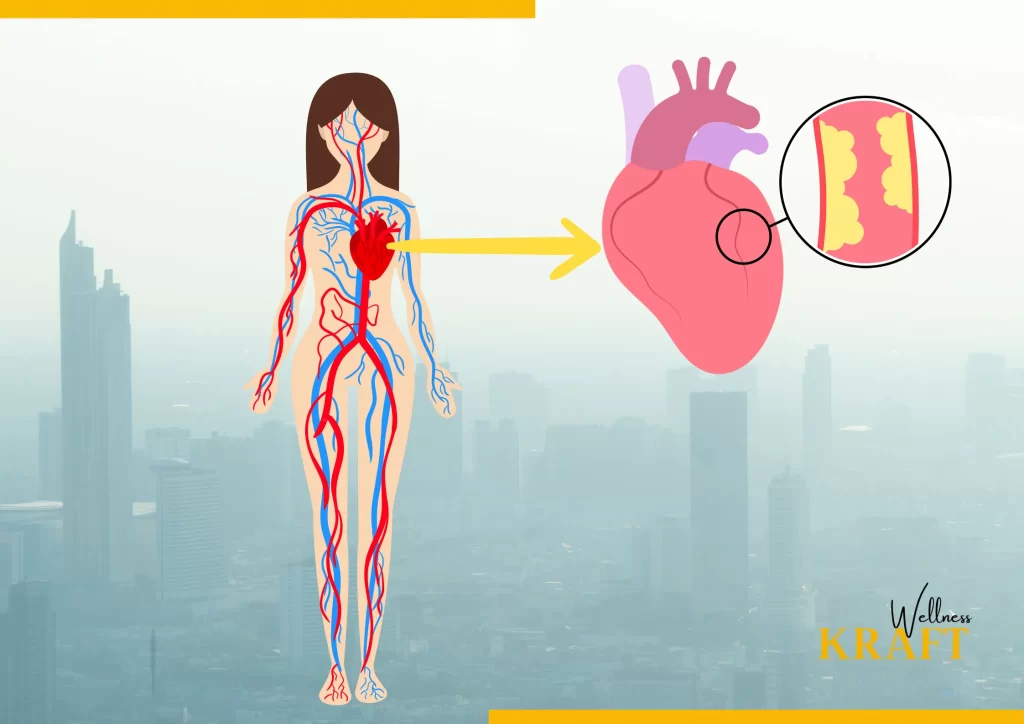
-Increased risk of heart disease
-Stroke
Air pollution can also have significant impacts on cardiovascular health, which can particularly affect women. Exposure to air pollution has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
Particulate matter (PM) is one of the main pollutants in the air that can impact cardiovascular health. When inhaled, PM can enter the bloodstream and cause inflammation in the blood vessels, which can lead to the development of atherosclerosis, or the buildup of plaque in the arteries. This can increase the risk of heart disease, including heart attacks and coronary artery disease.
In addition to PM, exposure to nitrogen dioxide (NO2) has also been linked to an increased risk of heart disease and stroke. NO2 can cause inflammation in the blood vessels, which can increase blood pressure and decrease the amount of oxygen that reaches the heart.
Women may be particularly vulnerable to the cardiovascular health effects of pollution due to differences in physiology and hormone levels. For example, studies have shown that exposure to air pollution can lead to changes in hormone levels in women, which can further impact cardiovascular health.
Overall, the cardiovascular health effects of air pollution on women are significant and can have long-lasting consequences on overall health and well-being. It is important for individuals, policymakers, and industries to take steps to reduce air pollution and mitigate its negative impacts on cardiovascular health.
Mental Health Effects

-Depression
-Anxiety
Air pollution can also have impacts on mental health, particularly in women. Studies have shown that exposure to air pollution can lead to an increased risk of depression and anxiety.
One of the main mechanisms through which air pollution impacts mental health is through inflammation. Exposure can cause inflammation in the body, including in the brain, which can disrupt normal brain function and contribute to the development of depression and anxiety.
In addition to inflammation, it can also impact mental health through oxidative stress. When inhaled, air pollutants can lead to the production of reactive oxygen species, which can damage cells and contribute to the development of mental health disorders.
Women may be particularly vulnerable to the mental health effects of air pollution due to a variety of factors, including differences in physiology, hormone levels, and social factors. For example, studies have shown that women who are exposed to such pollution during pregnancy may be at increased risk of developing depression and anxiety postpartum.
Overall, the mental health effects on women are an important area of concern. It is important for individuals, policymakers, and healthcare providers to take steps to reduce pollution and mitigate its negative impacts on mental health. This may include measures such as reducing exposure to air pollution through personal protective equipment or changes in transportation and energy policies.
Environmental Justice

-Women as a vulnerable population
-Disproportionate exposure pollution
Environmental justice is a critical issue when it comes to the impacts of air pollution on women’s health. Women are often considered a vulnerable population when it comes to environmental risks, including exposure to air pollution.
One reason for this is that women may be disproportionately exposed to air pollution due to a variety of factors, including differences in occupational and residential patterns, as well as social and economic factors. For example, women may be more likely to work in occupations that expose them to air pollution, such as in the service or manufacturing industries.
In addition, women may also be more likely to live in areas with high levels of pollution due to factors such as poverty, racial discrimination, and lack of access to transportation. This can have a disproportionate impact on the health of women and their families, as they may be exposed to higher levels of air pollution on a daily basis.
Overall, the issue of environmental justice is an important consideration when it comes to understanding the impacts of such pollution on women’s health. Efforts to address this issue may include policies and interventions aimed at reducing exposure to air pollution, improving access to healthcare and other resources, and promoting social and economic equity.
Research Analysis
There is a growing body of authentic research on the effects of air pollution on women’s health. Here are a few significant findings from recent research:
A study published in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives found that exposure to air pollution during pregnancy was associated with an increased risk of preterm birth and low birth weight.
Another study published in the journal Environmental Science and Pollution Research found that women who lived in areas with higher levels of air pollution had a higher risk of developing gestational diabetes.
A review of the literature on air pollution and women’s reproductive health, published in the journal Reviews on Environmental Health, concluded that there is strong evidence linking exposure to air pollution with reduced fertility, pregnancy complications, and adverse birth outcomes.
A study published in the journal Stroke found that exposure to fine particulate matter air pollution was associated with an increased risk of stroke among women.
A study published in the journal Environmental Research found that women who lived in areas with higher levels of air pollution had an increased risk of developing depression.
These are just a few examples of the many studies that have been conducted on the impacts of air pollution on women’s health. Overall, the research suggests that exposure can have a wide range of negative health effects on women, from respiratory problems to reproductive and cardiovascular issues, and even mental health impacts.
Country Wise Comparison on Women Being Effected by Air Pollution
There is a growing body of research on the impact of air pollution on women’s health across different countries. While the specific effects may vary depending on factors such as the level of pollution, the health status of the population, and the quality of healthcare services, there are some general trends that have been observed.
In India, for example, studies have shown that women who are exposed to higher levels of air pollution are at an increased risk of experiencing pregnancy complications, such as preterm birth and low birth weight. Similarly, in China, exposure has been linked to a higher incidence of cardiovascular disease among women.
In the United States, studies have found that women who live in areas with high levels of such pollution are more likely to develop respiratory diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). They may also be at a higher risk of experiencing adverse birth outcomes, such as preterm birth and low birth weight.
Overall, it is clear that women are particularly vulnerable to the health effects of air pollution, and that this vulnerability can vary depending on a range of factors. Therefore, it is important for policymakers, healthcare providers, and individuals to take steps to reduce air pollution and protect women’s health.
Precautions

While it is a serious issue, there are steps that women can take to reduce their exposure and minimize its harmful effects on their health. Here are some precautions that women can take:
Stay informed: Stay up-to-date on air quality reports in your area and plan outdoor activities accordingly.
Wear protective gear: When outdoors, wear a mask designed to filter out pollutants, such as an N95 mask.
Limit outdoor activities: Reduce your time spent outdoors during times of high air pollution.
Keep indoor air clean: Use air purifiers and keep windows closed during times of high air pollution.
Avoid smoking: Avoid smoking cigarettes or being exposed to secondhand smoke.
Use eco-friendly products: Use eco-friendly cleaning products and avoid using pesticides or other harmful chemicals.
Reduce energy consumption: Use energy-efficient appliances and reduce your overall energy consumption to help reduce air pollution.
Promote clean air: Advocate for clean air policies in your community and support efforts to reduce air pollution.
Concluding Thoughts
In conclusion, the impacts of air pollution on women’s health are a significant public health concern. Women are particularly vulnerable to the health effects of such pollution due to a variety of factors, including differences in physiology and exposure patterns.
It is important to address the issue and its impacts on women’s health through a range of strategies, including policies aimed at reducing air pollution, promoting environmental justice, and improving access to healthcare and other resources.
At Wellness Kraft, we believe that raising awareness about the impacts of air pollution on women’s health is critical to improving public health outcomes. Our articles on women’s health provide valuable information and insights into this important issue, and we encourage readers to learn more about the ways in which air pollution can impact women’s health.
Key Takeaways
1.Women are particularly vulnerable to the negative health effects of air pollution, especially pregnant women and those with pre-existing health conditions.
2.Exposure to such pollution can lead to a wide range of health problems in women, including respiratory issues, reproductive complications, cardiovascular disease, and mental health disorders.
3.There is a growing body of evidence linking air pollution exposure to adverse birth outcomes, such as preterm birth and low birth weight.
4.Environmental justice is an important consideration when it comes to such type of pollution and women’s health, as women from low-income and marginalized communities may be disproportionately exposed to pollution.
5.Mitigating air pollution requires a multi-pronged approach, including policy interventions, technological innovations, and individual actions to reduce emissions and exposure.
FAQs
1.How does air pollution affect women’s respiratory health?
Exposure can cause or worsen respiratory issues such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and lung cancer in women.
2.Can air pollution affect women’s reproductive health?
Yes, exposure has been linked to infertility, pregnancy complications, and adverse birth outcomes such as low birth weight.
3.Does air pollution increase the risk of cardiovascular disease in women?
Yes, exposure has been shown to increase the risk of heart disease and stroke in women.
4.Are pregnant women more susceptible to the health effects of air pollution?
Yes, pregnant women are particularly vulnerable to the negative health effects of air pollution, as exposure can harm both the mother and developing fetus.
5.What are some mental health effects of air pollution on women?
Exposure has been associated with depression and anxiety in women.
6.How can women reduce their exposure to air pollution?
Women can reduce their exposure to such pollution by avoiding high-traffic areas, using air purifiers, and wearing masks in polluted environments.
7.Are women from certain communities more at risk of exposure to air pollution?
Yes, women from low-income and marginalized communities may be disproportionately exposed to such pollution due to factors such as proximity to industrial areas and lack of access to clean air resources.
8.How can policymakers address the effects of air pollution on women’s health?
Policymakers can address the effects on women’s health by implementing regulations and incentives to reduce emissions and promote cleaner technologies, as well as increasing access to healthcare and resources for affected communities.
9.What are some technological innovations to reduce air pollution?
Technological innovations include electric vehicles, renewable energy sources, and carbon capture and storage technology.
10.What can individuals do to reduce air pollution?
Individuals can reduce such pollution by using public transportation or carpooling, conserving energy, and properly disposing of waste.