“Anxiety just saps today’s energy; it does not empty tomorrow’s grief.” – Wellness Kraft
Table of Contents

Introduction
Are you or someone you know experiencing constant worry, fear, or unease? If yes, then it is possible that you or they might be suffering from an anxiety disorder. Millions of individuals all over the world suffer from anxiety disorders, one of the most prevalent mental health issues. They can cause significant distress and impact a person’s ability to carry out their daily activities. However, with the right understanding and treatment, anxiety disorders can be managed effectively.
In this article, we will explore the symptoms, causes, and treatments of anxiety disorders in detail. So, let’s dive in and learn more about Understanding Anxiety Disorders: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments.
What are Anxiety Disorders?
Anxiety disorders refer to a group of mental health conditions that cause excessive fear, worry, and unease. People with such disorders experience these feelings persistently and may feel powerless to control them. They may also have physical symptoms like sweating, shaking, increased heart rate, and muscle tension. It can interfere with a person’s ability to function in their daily life and negatively affect their relationships, work, and other important aspects of life.
Types of Anxiety Disorders
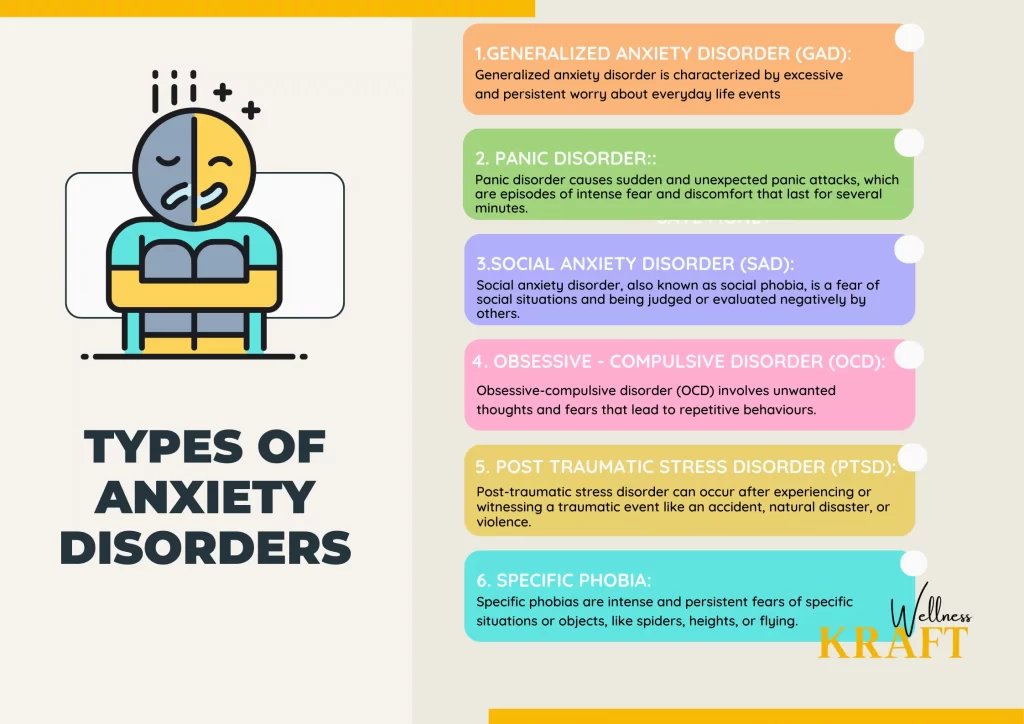
There are several types of anxiety disorders, and each type has its specific symptoms and causes. The most common ones include:
1. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD):
Generalized anxiety disorder is characterized by excessive and persistent worry about everyday life events, such as work, health, and relationships. People with GAD may also experience physical symptoms like muscle tension, restlessness, and fatigue.
2. Panic Disorder:
Panic disorder causes sudden and unexpected panic attacks, which are episodes of intense fear and discomfort that last for several minutes. Panic attacks can cause physical symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, and palpitations.
3. Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD):
Social anxiety disorder, also known as social phobia, is a fear of social situations and being judged or evaluated negatively by others. People with SAD may avoid social situations or endure them with significant distress.
4. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD):
Obsessive-compulsive disorder is characterized by intrusive and persistent thoughts, impulses, or images (obsessions) that cause anxiety and repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions) that the person feels compelled to perform to relieve their anxiety.
5. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD):
Post-traumatic stress disorder can occur after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event like an accident, natural disaster, or violence. People with PTSD may experience flashbacks, nightmares, and avoid situations that remind them of the traumatic event.
6. Specific Phobias:
Specific phobias are intense and persistent fears of specific situations or objects, like spiders, heights, or flying.
The symptoms of anxiety disorders can vary depending on the type of anxiety disorder
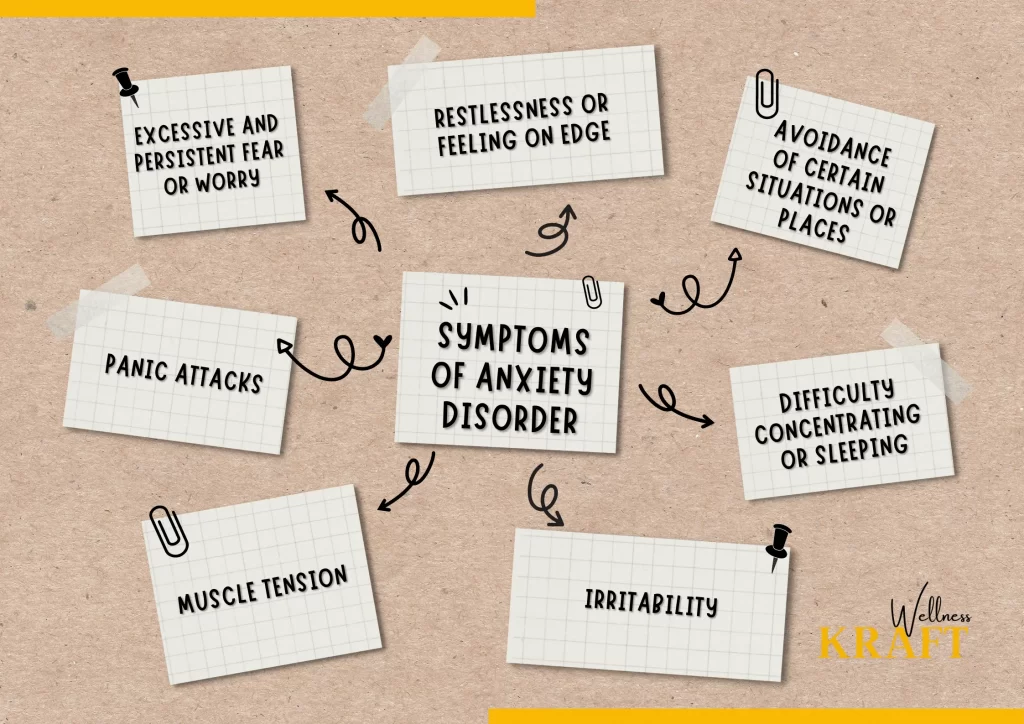
However, some common symptoms include:
• Excessive and persistent fear or worry
• Restlessness or feeling on edge
• Irritability
• Muscle tension
• Difficulty concentrating or sleeping
• Panic attacks
• Avoidance of certain situations or places
Anxiety disorders are complex conditions, and their causes are not entirely understood. However, research suggests that several factors can contribute to the development of such disorders.
Some of the Most Common Causes of Anxiety Disorders are as Follows
1. Genetics:
Studies suggest these disorders can run in families. People with a family history are more likely to develop anxiety themselves.
2. Brain Chemistry:
The imbalance of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that transmit signals in the brain, can lead to anxiety disorders. An excess of certain neurotransmitters like norepinephrine and serotonin can cause anxiety symptoms.
3. Environmental Factors:
Traumatic life events such as abuse, neglect, or violence can trigger anxiety disorders. Chronic stress, relationship problems, financial difficulties, and other life stressors can also contribute to the development of such disorders.
4. Medical Conditions:
Chronic medical conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, or thyroid problems can cause anxiety symptoms. Anxiety disorders are also possible outcomes of drug or pharmaceutical addiction or withdrawal.
These disorders are not the result of a lack of strength of character or the inability to control one’s emotions. They are legitimate medical conditions that require appropriate treatment and care.
Treatments of Anxiety Disorders
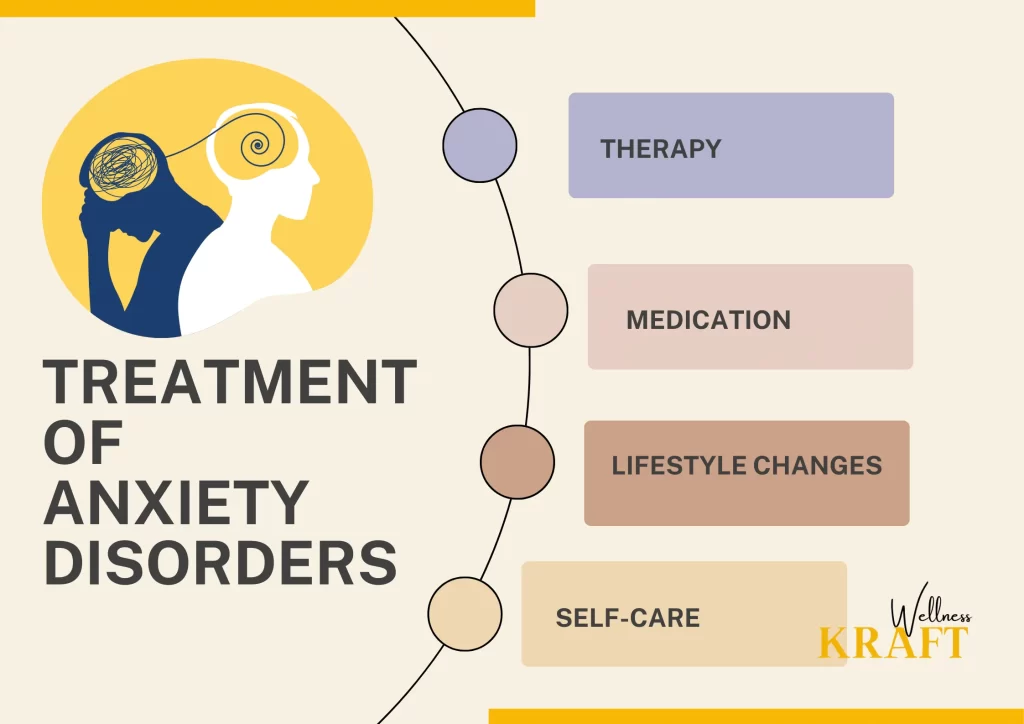
These disorders can be challenging to manage, but there are several effective treatments available. They are often treated with a multifaceted approach that includes psychotherapy, medication, and behavioural modifications. Common treatments include:
1. Therapy:
Psychotherapy or talk therapy is a highly effective treatment for anxiety disorders. The most common treatment is cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). Altering negative ways of thinking and acting that bring on anxiety is the main focus here. Other forms of therapy, such as exposure therapy, can also be helpful for anxiety disorders.
2. Medication:
Several types of medications can be used to treat such disorders. Antidepressants such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are commonly prescribed. Benzodiazepines, which are sedatives, can also be prescribed for short-term use. However, they can be addictive and are usually not recommended for long-term use.
3. Lifestyle Changes:
Certain lifestyle changes can help manage anxiety symptoms. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine can help manage anxiety symptoms.
4. Self-Care:
Practicing self-care is essential for managing anxiety. Activities such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help reduce anxiety symptoms. Relaxation techniques such as yoga, massage, and aromatherapy can also be helpful.
Concluding Thoughts
In conclusion, Understanding Anxiety Disorders: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments is essential for promoting mental wellness. Seeking knowledge and understanding of such disorders can help reduce the stigma associated with mental health and encourage individuals to seek help. At Wellnesskraft, we recognize the importance of providing resources and support for those struggling with anxiety disorders. With the right treatment and support, individuals can manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
We encourage anyone experiencing symptoms of an anxiety disorder to seek professional help and access the resources available to them. Together, we can work towards creating a more compassionate and understanding society for those with mental health conditions.
FAQs
1. What is an anxiety disorder?
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions that are marked by excessive and long-lasting feelings of worry, fear, and dread. They can interfere with daily life and can be debilitating if left untreated.
2. How do you know if you have an anxiety disorder?
Depending on the type of anxiety disease, the signs can be different.However, common symptoms include excessive worrying, restlessness, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and physical symptoms such as heart palpitations, sweating, and trembling.
3. Can anxiety disorders be cured?
Anxiety disorders cannot be cured, but they can be managed effectively with appropriate treatment. The treatment may include therapy, medicine, and changes in how you live your life.
4. Can anxiety disorders develop suddenly?
Anxiety disorders can develop suddenly, but they can also develop gradually over time. Traumatic life events, such as the death of a loved one or a serious accident, can trigger the sudden onset of an anxiety disorder.
5. Who is at risk for developing an anxiety disorder?
Anyone can develop an anxiety disorder, but certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing one. These include a family history of anxiety disorders, a history of trauma or abuse, chronic medical conditions, and substance abuse.
6. How is an anxiety disorder diagnosed?
Anxiety disorders are diagnosed by a mental health professional, usually a psychologist or psychiatrist. Diagnosis is based on a thorough evaluation of symptoms, medical history, and a psychological assessment.
7. Can anxiety disorders be prevented?
There is no known way to prevent anxiety disorders, but certain lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of developing one. These include regular exercise, healthy eating, getting enough sleep, and avoiding drugs and alcohol.
8. Are there any natural remedies for anxiety disorders?
Several natural remedies, such as herbal supplements, relaxation techniques, and aromatherapy, can help manage anxiety symptoms. But it’s important to consult a healthcare professional before using any natural treatments.
9. How long does it take to recover from an anxiety disorder?
The length of time it takes to recover from an anxiety disorder varies depending on the individual and the severity of the disorder. With appropriate treatment, many people can manage their symptoms and live fulfilling lives.
10. What can I do to help a loved one with an anxiety disorder?
If you have a loved one with an anxiety disorder, it is essential to provide support and understanding. Encourage them to seek treatment, and be patient and compassionate as they work through their symptoms.







1 comment