” The fact that I have PCOS is only a small part of who I am. Having PCOS is a fight, but I’m ready for it.” – Wellness Kraft
Introduction
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complicated hormonal disease that affects many women around the world. It is marked by small cysts on the ovaries, menstrual cycles that come and go, and too much of the hormone androgen. The health of a woman can be affected by PCOS in a number of ways, including fertility issues. In this article, we’ll look at how PCOS and fertility treatments are linked.
The effects of PCOS on fertility, common symptoms, and PCOS diagnostic criteria will be covered in detail. We will also talk about lifestyle changes, medications, and the various fertility treatment options for women with PCOS. Women with PCOS can make smart choices and get the right treatment to increase their chances of getting pregnant by learning about the different parts of the condition and its treatment.
How to Understand PCOS and How It Affects Fertility
– A woman’s fertility may be negatively impacted by polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). To understand its effects, it is important to understand how PCOS works and how it affects the reproductive system.
PCOS is caused by hormonal problems, especially high amounts of androgens like testosterone. These changes can make it hard for a woman to ovulate normally, which can cause her menstrual cycles to be irregular or stop altogether. In PCOS, the ovaries may get small cysts, which are follicles that don’t grow and release eggs.
– Women with PCOS who are trying to get pregnant face a serious challenge because they don’t ovulate regularly. During ovulation, a developed egg moves out of the ovary so that it can be fertilized by sperm. If a woman doesn’t ovulate, her chances of getting pregnant and having a baby are lower.
-The hormonal issues that come with PCOS can also change the quality of the eggs that are made. The eggs may have a lower chance of getting fertilized or have problems with their chromosomes, which makes the risk of miscarriage higher.
-Also, the high amounts of androgens in PCOS can stop the development of the lining of the uterus, making it less open to the implantation of an embryo. Even if the egg is fertilised, the baby may have trouble implanting and starting a pregnancy.
-Not all women with PCOS will experience infertility; it’s important to remember this. Some women may still ovulate irregularly or get pregnant without any help from a doctor. However, there are many options available to improve fertility and increase the chances of getting pregnant for those who are having trouble.
-The common symptoms and signs of PCOS, as well as the lifestyle changes, medications, and treatment criteria that can help overcome PCOS-related symptoms, will be covered in the parts that follow. Women can take proactive steps towards starting families by addressing the unique concerns of PCOS-related infertility.
Common PCOS Symptoms

1) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disease with many different signs and symptoms. There are some common signs that health care providers look for when diagnosing PCOS, despite the fact that symptoms can change from person to person.
2) One of the defining symptoms of PCOS is an irregular menstrual cycle. Women with PCOS often have menstrual problems, such as long or unpredictable periods or even no periods at all (amenorrhea). Hormonal problems, which stop ovulation from occurring normally, are the root of these issues.
3) Hirsutism, which means too much hair growth, is another common sign of PCOS. This usually happens to guys, with more hair growing on the face, chest, stomach, and back. Also, your hair may be thicker and darker than normal. Women who have PCOS may also lose hair or have it thin out on the head.
4) PCOS often causes acne, which is another common sign. Hormonal imbalances, especially high amounts of the hormone androgen, can cause more sebum to be made and clogged pores, which can lead to acne, especially on the face, chest, and upper back.
Women with PCOS frequently experience weight gain and trouble losing weight. Insulin resistance, a condition in which the body doesn’t use insulin as well as it should, is often present in PCOS and adds to weight issues. Even if women with PCOS try to live a healthy lifestyle, it may be hard for them to control their weight.
Medication and Treatments for Infertility Caused By PCOS
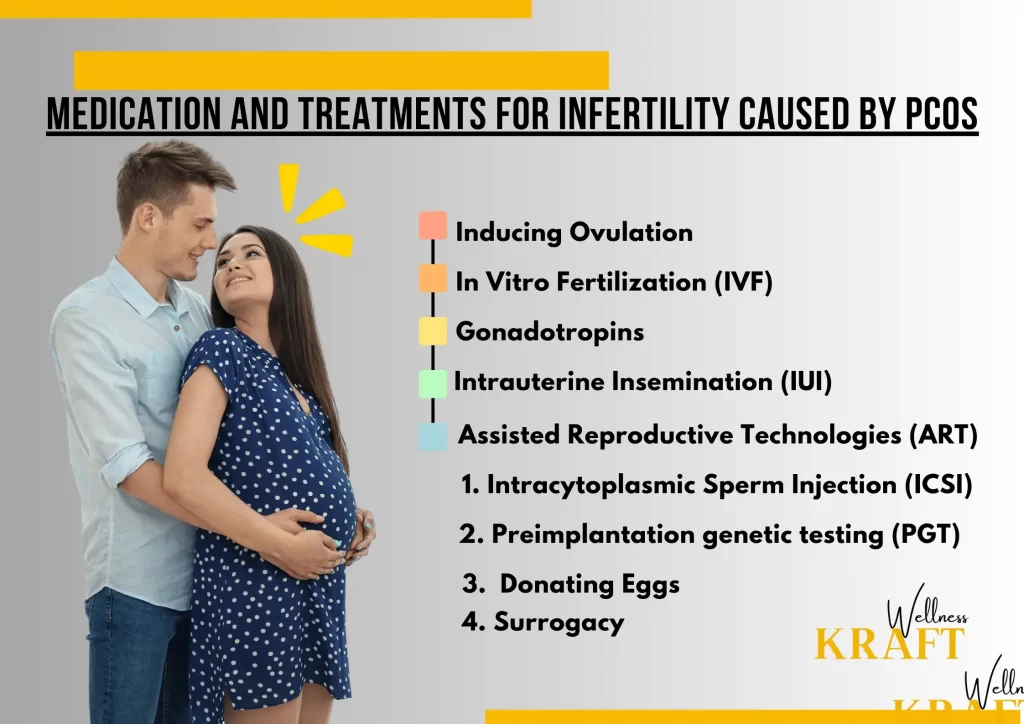
In addition to making changes to their lifestyle, women with PCOS can also use medications and other treatments to help them get pregnant. These treatments are meant to help with certain aspects of infertility caused by PCOS. Here are a few common options:
1. Inducing ovulation:
Drugs like clomiphene citrate or letrozole may be given to make ovulation happen. These medications help control hormone levels and make it easier for mature eggs to come out.
Ovulation stimulation can be a helpful fertility treatment for women with polycystic ovary syndrome who have trouble ovulating regularly. For ovulation induction, medications are used to stimulate the ovaries and help them make and release mature eggs.
Clomiphene citrate, also referred to as Clomid, is a common prescription drug used to induce ovulation. Clomiphene citrate works by stopping estrogen receptors in the brain from doing their job. This makes more follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) come out of the body. The ovarian follicles, which hold the eggs, grow and mature with the help of these hormones.
2. Hormones that are injected:
Sometimes, medications like gonadotropins that are given by injection are used to make ovulation happen. This type of treatment is usually used when oral medications don’t work.
3. Intrauterine Insemination (IUI):
Intrauterine insemination, or IUI, is a common fertility treatment that can be used alone or in conjunction with ovulation induction. It involves putting specially prepared sperm straight into the uterus. This way, the sperm doesn’t have to go through the cervix and into the fallopian tubes.
Before IUI, the male partner or a sperm donor gives a sample of sperm, which is then washed in a process called “sperm washing.” Sperm washing removes the healthy, moving sperm from the semen and gets rid of any debris or substances that could cause irritation.
During IUI, the cleaned sperm are put into the uterus with the help of a thin, flexible catheter. This is usually done right after ovulation, when the egg that was released is most likely to be in the fallopian tubes.
4. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF):
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a very advanced and successful fertility treatment that can be especially helpful for women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) who haven’t been able to get pregnant any other way. IVF involves putting eggs and sperm together outside of the body, in a lab, and then putting the resulting babies into the uterus.
Most of the time, there are several steps to the IVF process. In order to encourage the growth of multiple follicles and the production of more eggs, ovarian stimulation is first performed using injectable medications. This is especially important for women with PCOS, who may have a higher number of eggs that haven’t fully grown yet.
Next, the eggs are taken out of the ovaries using a simple surgery called transvaginal ultrasound-guided follicle aspiration. The sperm is then added to the eggs in a lab, either using traditional IVF or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), in which a single sperm is put straight into each egg.
The resulting eggs are kept an eye on and given a few days to grow in the lab. Before choosing which eggs to transfer, the medical team will look at the quality and health of each one. The chosen embryos are then put into the uterus through a thin catheter, where they may implant and lead to a baby.
5. Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART):
In addition to IVF, other ART methods like intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) or preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) may be suggested, depending on the person’s case. As alternative options or in conjunction with other treatments, these ART procedures are frequently used. Here are some common options for ART:
1. Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI):
In ICSI, a single sperm is injected directly into an egg to help it become fertilized. It is especially helpful for couples dealing with the male factor in fertility or when there are issues with sperm quality or number.
2. Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT):
Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) is a test done on IVF-created embryos to look for chromosomal problems or genetic diseases. This helps choose the best embryos to transfer, which could improve the chances of getting pregnant.
3. Donating eggs:
Donating eggs from a healthy donor may be a choice for women with PCOS who have poor egg quality or low ovarian reserve. The sperm from the partner or donor is used to fertilise the given eggs, which are then put into the uterus of the recipient.
4. Surrogacy:
A woman with PCOS might want to use a surrogate mother if she can’t or shouldn’t carry a baby herself. In surrogacy, a different woman holds the baby for the parents who want it.
It’s important to talk to a fertility specialist or reproductive endocrinologist about the ART options that will work best for you. They will look at your personal situation, give you guidance on the best ART procedures, and support you the whole way through the process.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
In addition to traditional medical treatments, some alternative and complementary therapies may be explored to support fertility in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. These therapies may not treat PCOS directly or guarantee pregnancy, but they may improve overall well-being, reduce stress, and encourage hormonal balance. Here are some alternative and complementary therapies that can be tried:
1. Acupuncture:
In acupuncture, fine needles are put into certain spots on the body to increase energy flow and bring the body back into balance. For some women with PCOS, it may help control menstrual cycles, lessen stress, and improve cycle results.
2. Supplements:
Chasteberry (Vitex agnus-castus) and cinnamon are two examples of plant supplements that have been used for a long time to support hormonal balance and menstrual regularity. But before taking any herbal supplements, it’s important to talk to a health care provider about their safety and effectiveness.
3. Mind-Body Techniques:
Activities like yoga, meditation, and mindfulness-based stress reduction can help you deal with worry, enhance your mental well-being, and relax. Indirectly, these methods may help fertility by lowering the amount of stress hormones in the body and restoring hormonal balance overall.
4. Dietary Supplements:
Some dietary supplements, like inositol and omega-3 fatty acids, may help women with PCOS control their insulin resistance and hormone levels. To ensure proper dosage and suitability, it’s important to talk to a health care expert or qualified dietitian before starting any supplements.
It’s important to remember that alternative and complementary therapies should be used in conjunction with traditional medical treatments and under the guidance of health care professionals. Different people may react differently to these therapies, so it’s important to stay in touch with your healthcare team as you go through the process.
Concluding Thoughts
In conclusion, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can have a big effect on women’s fertility. It is a complicated disease that causes hormonal imbalances, irregular menstrual patterns, and cysts on the ovaries. But women with PCOS can improve their chances of getting pregnant and having a healthy baby if they take the right steps and get the right treatments.
This piece has given some information about the link between PCOS and infertility. It has shown how PCOS can affect ovulation and make it harder for women to get pregnant. The value of early detection and accurate diagnosis has been emphazised as we have discussed the common PCOS symptoms and diagnostic criteria.
We have also looked into different strategies to improve PCOS fertility. A healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and maintaining a healthy weight are just a few examples of lifestyle changes that can improve hormone balance and reproduction.
Also, we’ve talked about some of the common medications and treatments for infertility caused by PCOS. The use of medications like clomiphene citrate, which induces ovulation, can increase the likelihood of ovulation by stimulating egg production. Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a procedure that can help bring the sperm closer to the eggs, which makes fertilization more likely.
In vitro fertilization (IVF) and other assisted reproductive technologies (ART) can be very good options for women who haven’t been able to get pregnant with other methods. Many of the issues related to PCOS-related infertility can be overcome by these cutting-edge procedures, which have higher success rates.
Lastly, we briefly discussed alternative and complementary therapies that can be used as support for women with PCOS and fertility issues. Acupuncture, herbal supplements, mind-body techniques, and dietary supplements may be used in conjunction with traditional treatments to enhance overall well-being.
When writing this piece, I relied on reliable sources and what I knew about the topic. It is always best to speak with a health care professional or reproductive expert for more detailed information and personalized guidance.
Key Takeaways
1. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal condition that can have a big effect on women’s fertility.
2. PCOS is characterized by hormonal imbalances, irregular menstrual periods, and cysts on the ovaries.
3. A healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and keeping a healthy weight are just a few lifestyle changes that can help women with PCOS improve their fertility.
4. Medications and treatments like ovulation induction and intrauterine insemination (IUI) can be used to stimulate ovulation and improve the chances of getting pregnant.
5. In vitro fertilization (IVF) and other assisted reproductive technologies (ART) are very good options for women who haven’t had luck with other treatments.
6. Alternative and complementary therapies, such as acupuncture and mind-body techniques, may offer extra support for women with PCOS in terms of fertility.
7. The way each woman responds to treatments and therapies may be different, so it’s important to keep lines of communication open with health care workers.
FAQs
1. Is PCOS a common health problem?
Yes, it is a common hormonal problem that affects a lot of women of childbearing age. It is thought that about one in ten women around the world may have PCOS.
2. What are the most common PCOS symptoms?
Irregular menstrual cycles, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), acne, weight gain or trouble losing weight, and cysts on the ovaries are the main symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome. But the symptoms can be different for each person.
3. Can blood tests tell if someone has PCOS?
Even though there is no one test that can tell for sure if someone has polycystic ovary syndrome, blood tests can help find out. Hormones like follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), testosterone, and insulin may be measured during these tests. Also, an ultrasound might be used to look at the ovaries and see if there are any cysts.
4. Is infertility always a result of PCOS?
Even though polycystic ovary syndrome doesn’t always cause infertility, it can make it harder to get pregnant. Women with such symptoms often don’t ovulate on time or at all, which can make it harder for them to get pregnant. But with the right treatments, many women with polycystic ovary syndrome can have healthy babies.
5. What changes in lifestyle can help PCOS women’s fertility?
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome may benefit from adopting a healthier lifestyle. This includes eating a well-balanced diet, getting regular exercise, dealing with stress, and staying at a healthy weight. These changes to your lifestyle can help control hormone levels and improve the way your body reproduces.
6. For infertility caused by PCOS, what are the treatment options?
Ovulation induction with medications like clomiphene citrate, intrauterine insemination (IUI), and in vitro fertilization (IVF) are some of the possible treatment options for PCOS-related infertility. Choosing a treatment rests on a number of factors and should be made to fit the needs of each person.
7. Can acupuncture and other alternative therapies, such as PCOS, help with fertility?
For women with polycystic ovary syndrome and fertility problems, alternative therapies like acupuncture may offer extra support. Acupuncture can help regulate menstrual cycles, lower stress levels, and support hormonal balance. But it’s important to talk to a qualified acupuncturist and a health care professional about these options.
8. Are there any natural products that women with PCOS can take to improve their fertility?
Some natural products, like inositol and omega-3 fatty acids, have shown promise in treating PCOS symptoms and improving fertility. To ensure safety, proper dosage, and suitability, it is important to talk to a health care expert before beginning any supplements.
9. Can you get rid of PCOS?
PCOS is a long-term disease that can’t be cured, but its symptoms and effects can be managed. Women with PCOS can live healthy lives and increase their chances of getting pregnant with the right treatments and lifestyle changes.
10. When should I get help from a doctor if I think I have PCOS?
It is advised to seek medical help if you have symptoms like irregular periods, a lot of hair growth, acne, or trouble getting pregnant. A health care professional, like a gynecologist or reproductive endocrinologist, can assess your symptoms, run any necessary tests, and give you the right guidance and treatment options.





Join the conversation