“Thyroid problems have symptoms that are similar to those of other conditions. You must insist on getting the right diagnosis and therapy..” – Wellness Kraft
Introduction
Thyroid disorders are a group of medical conditions that affect the function of the thyroid gland, which is located in the neck and produces hormones that regulate metabolism and other vital bodily functions. These disorders can have a significant impact on women’s health, as they are more likely than men to develop thyroid problems. In this article, we will explore the different types of thyroid disorders, their symptoms, causes, and treatments, with a focus on women’s health. We will also provide some tips for managing thyroid disorders and improving overall health.
Table of Contents
What is the Thyroid Gland?
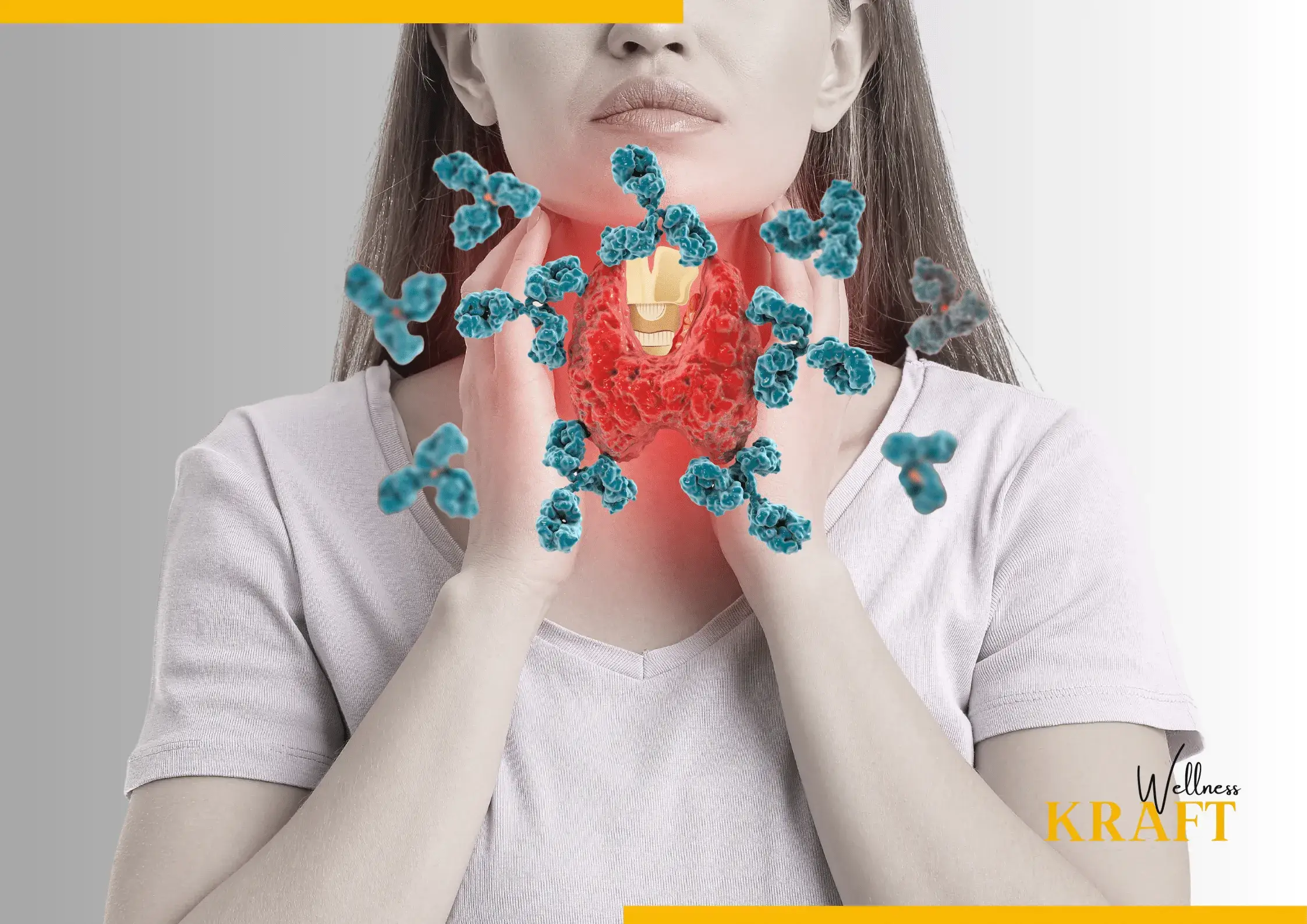
Located in the neck, the thyroid gland is a tiny, butterfly-shaped gland. It is responsible for producing thyroid hormones that regulate metabolism, energy levels, body temperature, and other vital bodily functions. The two main hormones produced by the thyroid gland are T3 and T4. These hormones play a critical role in regulating the body’s metabolism and energy levels.
Types of Thyroid Disorders
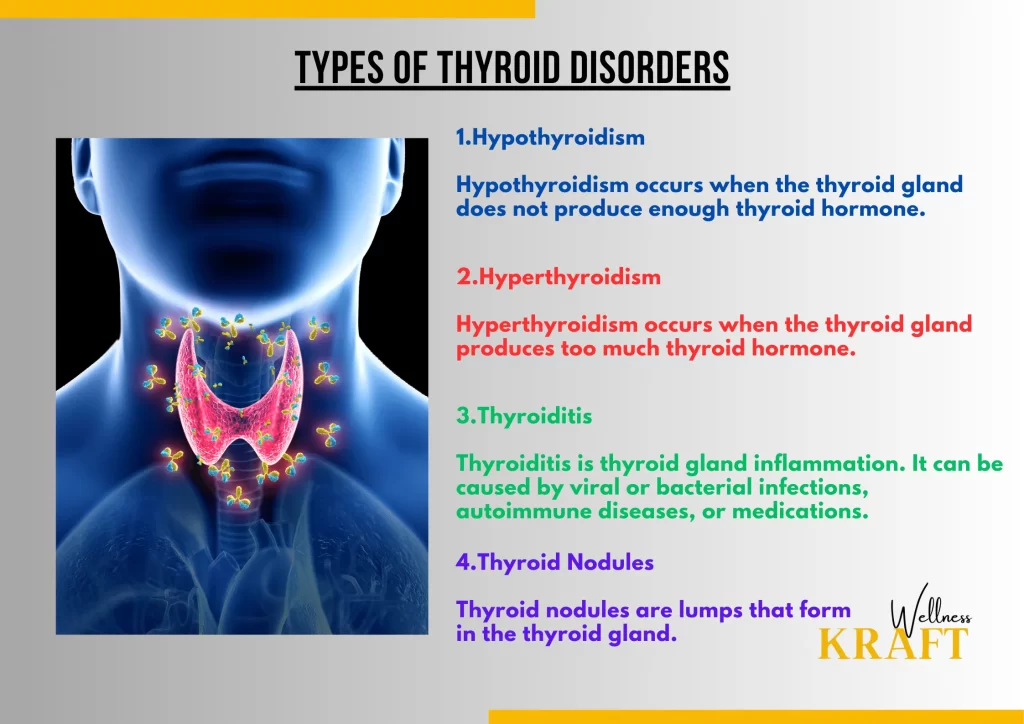
There are several types of thyroid disorders, including hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, thyroiditis, and thyroid nodules.
1.Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. This can lead to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, constipation, and depression. Hypothyroidism is more common in women than men and is usually caused by an autoimmune condition called Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
2.Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone. This can lead to symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, irritability, and heat intolerance. Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism.
3.Thyroiditis
Thyroiditis is thyroid gland inflammation. It can be caused by viral or bacterial infections, autoimmune diseases, or medications. Thyroiditis can cause symptoms of both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
4.Thyroid Nodules
Thyroid nodules are lumps that form in the thyroid gland. Most thyroid nodules are benign and do not cause any symptoms. However, some nodules can produce too much thyroid hormone, leading to hyperthyroidism.
Scientific Theory on Thyroid Disorder
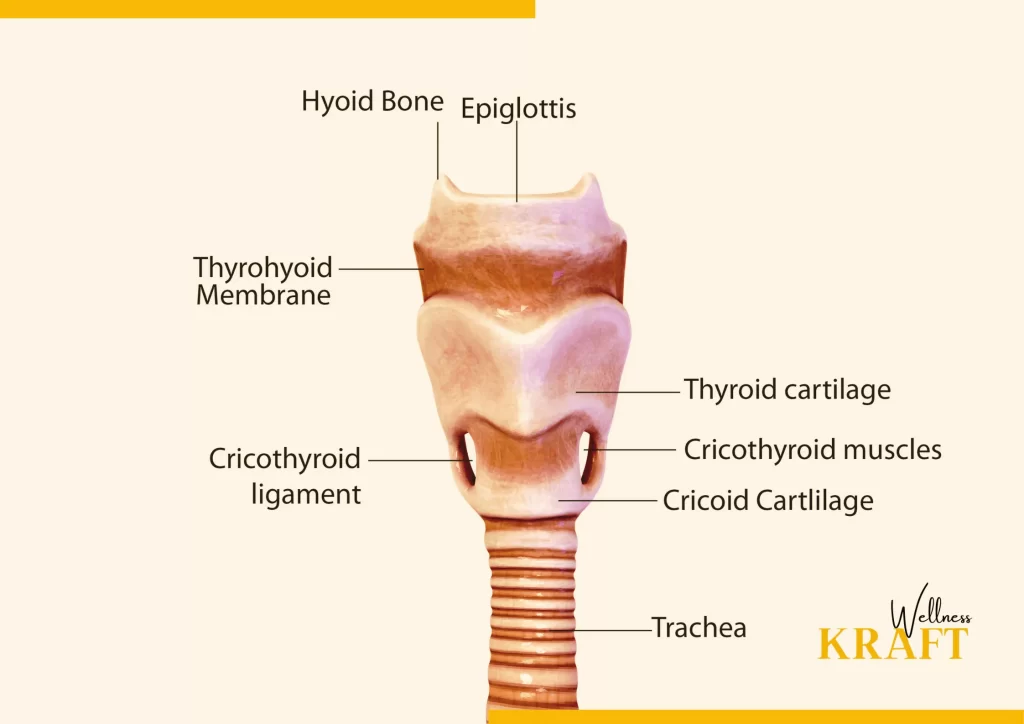
The scientific theory of thyroid disorder is based on the functioning of the thyroid gland, which is located in the neck and produces hormones that regulate metabolism. It can occur when the thyroid gland produces too much or too little of these hormones, leading to a range of symptoms and health problems.
One of the most common theories for the development of such disorders is an autoimmune response, where the body’s immune system attacks the thyroid gland. This can lead to inflammation and damage to the gland, causing it to produce too little or too much hormone. Autoimmune thyroid disorders, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease, are often the result of this mechanism.
Another theory for the development of thyroid disorders is related to iodine deficiency. Iodine is a mineral that is essential for the production of thyroid hormones, and low iodine levels can lead to an underactive thyroid. However, in developed countries where iodine deficiency is rare, other factors such as genetic predisposition and environmental factors may play a larger role in the development of thyroid disorders.
Other possible theories for the development of thyroid disorders include exposure to radiation, certain medications, and viral infections.
Overall, the scientific theory of thyroid disorders is complex and multifaceted, with many factors potentially contributing to their development. Further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms behind thyroid disorders and to develop more effective treatments for those affected.
Thyroid Disorders’ Causes

Thyroid issues in women can have a variety of causes. Here are a few of the most common ones:
1.Autoimmune diseases:
Autoimmune conditions including Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease are the most frequent causes of thyroid problems. These conditions cause the immune system to attack the thyroid gland, leading to either an underactive or overactive thyroid.
2.Iodine deficiency:
Iodine is a mineral that is necessary for the production of thyroid hormones. If a person’s diet is low in iodine, they may develop an underactive thyroid gland, known as hypothyroidism.
3.Thyroid nodules:
Thyroid nodules are lumps that grow on the thyroid gland. They can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and can cause an overactive or underactive thyroid gland.
4.Radiation therapy:
Radiation therapy to the neck or head can damage the thyroid gland and cause hypothyroidism.
5.Medications:
Some medications, such as lithium, interferon alpha, and amiodarone, can cause hypothyroidism.
6.Pregnancy:
During pregnancy, the body goes through many hormonal changes, which can sometimes lead to thyroid disorders.
7.Genetics:
Some thyroid disorders can be inherited, such as congenital hypothyroidism.
It’s important to note that in many cases, the cause of thyroid disorders is unknown.
Thyroid Disorders Symptoms
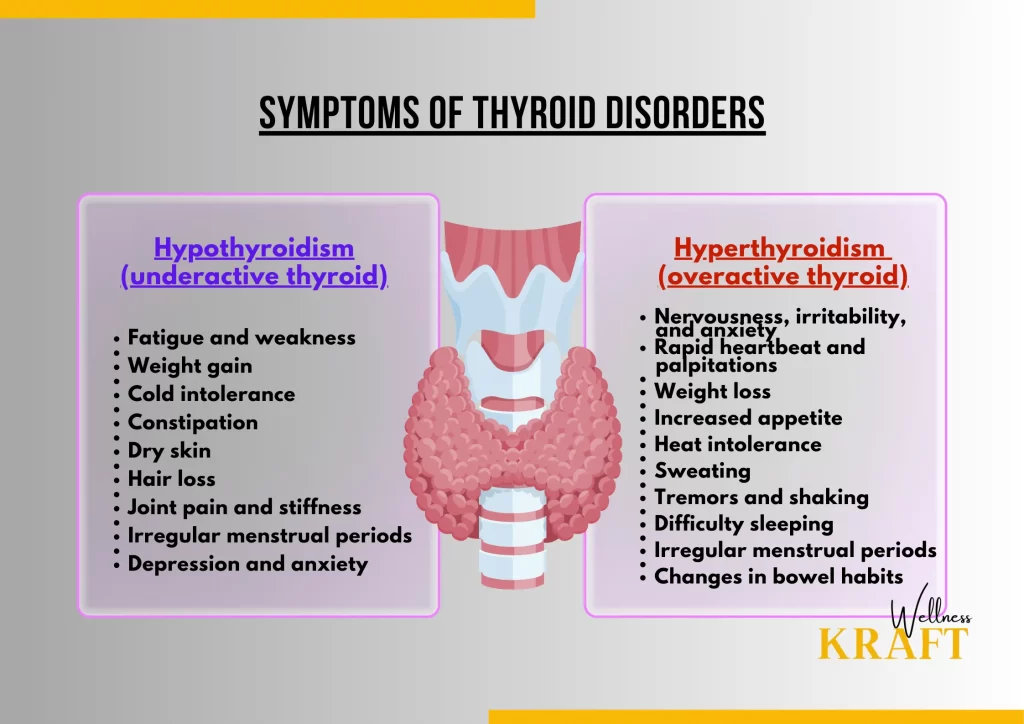
Thyroid disorders can cause a range of symptoms that vary depending on whether the thyroid gland is overactive or underactive. Here are some of the most common symptoms:
1.Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid):
Fatigue and weakness
Weight gain
Cold intolerance
Constipation
Dry skin
Hair loss
Joint pain and stiffness
Irregular menstrual periods
Depression and anxiety
2.Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid):
Nervousness, irritability, and anxiety
Rapid heartbeat and palpitations
Weight loss
Increased appetite
Heat intolerance
Sweating
Tremors and shaking
Difficulty sleeping
Irregular menstrual periods
Changes in bowel habits
In some cases, thyroid disorders can also cause other symptoms such as goiter (swelling of the thyroid gland), hoarseness, and difficulty swallowing. It’s important to note that not all people with thyroid disorders experience the same symptoms, and some may not have any symptoms at all.
Diagnosis
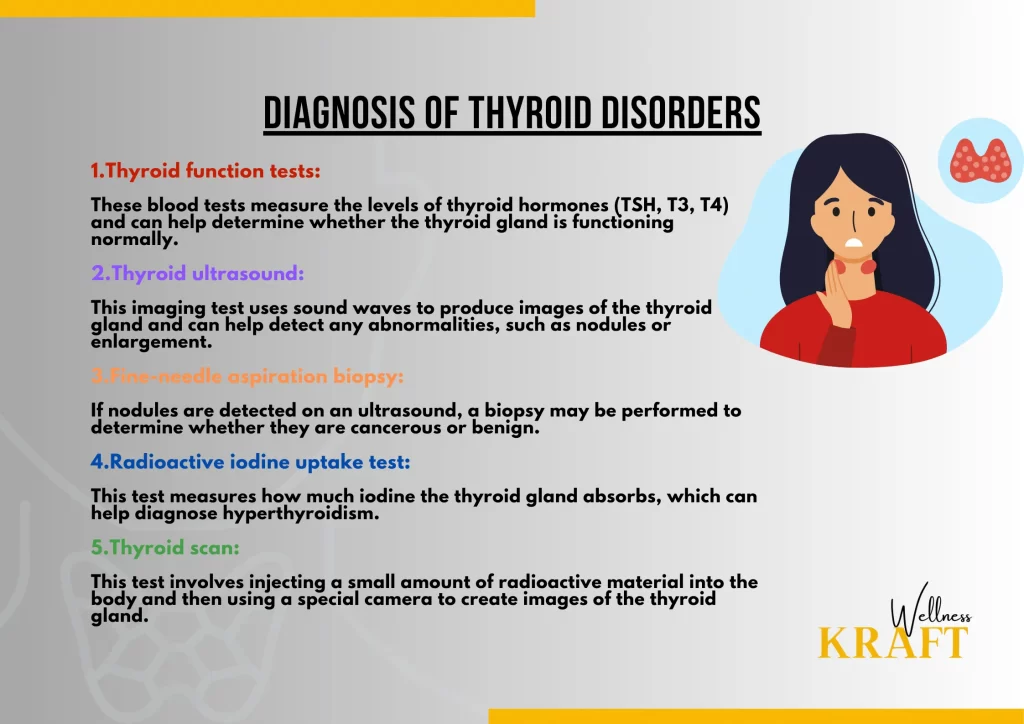
Diagnosing thyroid disorders involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. Here are some of the common tests used to diagnose thyroid disorders:
1.Thyroid function tests:
These blood tests measure the levels of thyroid hormones (TSH, T3, T4) and can help determine whether the thyroid gland is functioning normally.
2.Thyroid ultrasound:
This imaging test uses sound waves to produce images of the thyroid gland and can help detect any abnormalities, such as nodules or enlargement.
3.Fine-needle aspiration biopsy:
If nodules are detected on an ultrasound, a biopsy may be performed to determine whether they are cancerous or benign.
4.Radioactive iodine uptake test:
This test measures how much iodine the thyroid gland absorbs, which can help diagnose hyperthyroidism.
5.Thyroid scan:
This test involves injecting a small amount of radioactive material into the body and then using a special camera to create images of the thyroid gland. It can help detect any abnormalities in the gland’s structure or function.
If you are experiencing any symptoms of a thyroid disorder, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider who can help determine if further testing is necessary.
Treatment
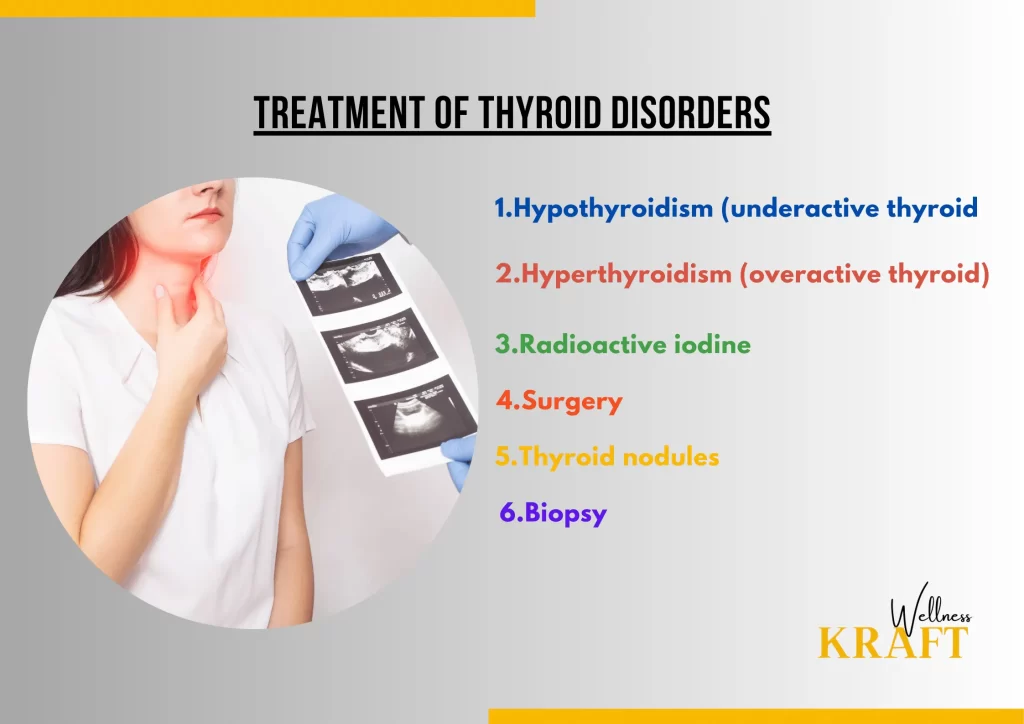
The kind and severity of a thyroid condition will determine how it is treated. Here are some of the common treatments for thyroid disorders:
1.Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid):
– Levothyroxine: This medication replaces the missing thyroid hormone in the body and is usually taken once a day.
2.Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid):
-Anti-thyroid medications: These medications block the production of thyroid hormones in the body.
3.Radioactive iodine:
This treatment involves swallowing a capsule or liquid that contains radioactive iodine, which destroys the thyroid gland.
4.Surgery:
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove all or part of the thyroid gland.
5.Thyroid nodules:
-Observation: In some cases, nodules may be monitored over time to see if they grow or change.
6.Biopsy:
If nodules are cancerous, surgery may be necessary to remove all or part of the thyroid gland.
It’s important to work with your healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan for your specific thyroid disorder. Additionally, once treatment is initiated, regular monitoring and follow-up appointments may be necessary to ensure that the treatment is effective and that hormone levels are within the normal range.
Natural Remedies
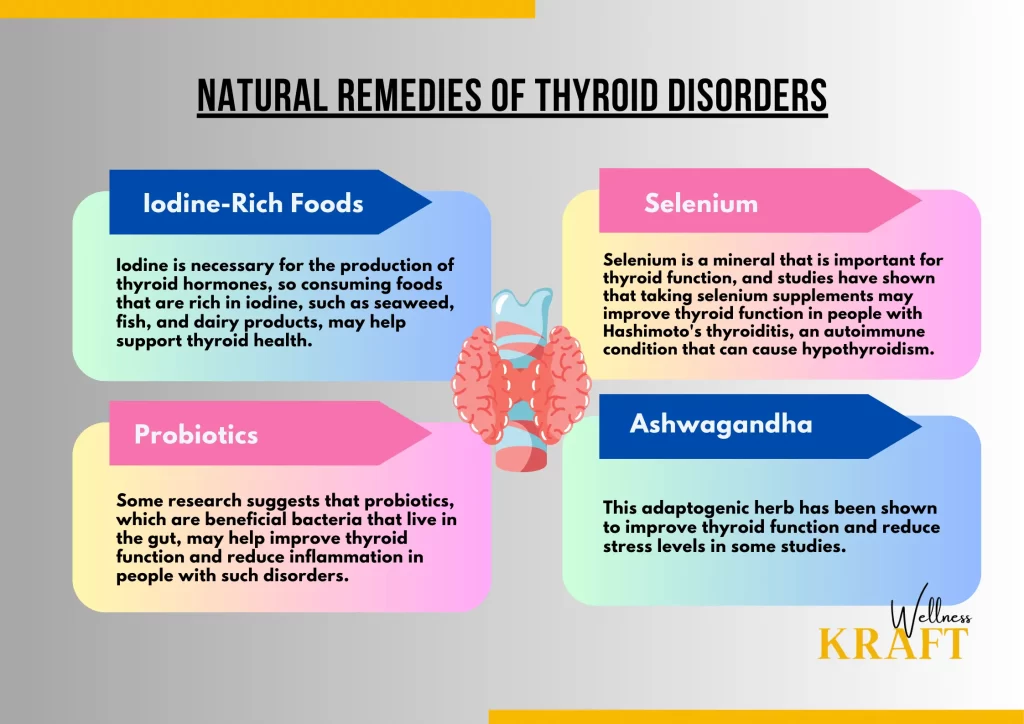
While medical treatment is often necessary for thyroid disorders, there are also some natural remedies that may help alleviate symptoms or support overall thyroid health. Here are some of the natural remedies that have been studied:
1.Iodine-rich foods:
Iodine is necessary for the production of thyroid hormones, so consuming foods that are rich in iodine, such as seaweed, fish, and dairy products, may help support thyroid health.
2.Selenium:
Selenium is a mineral that is important for thyroid function, and studies have shown that taking selenium supplements may improve thyroid function in people with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune condition that can cause hypothyroidism.
3.Probiotics:
Some research suggests that probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that live in the gut, may help improve thyroid function and reduce inflammation in people with such disorders.
4.Ashwagandha:
This adaptogenic herb has been shown to improve thyroid function and reduce stress levels in some studies.
It’s important to note that while these natural remedies may be helpful for some people, they should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment. Always talk to your healthcare provider before starting any new supplements or making significant changes to your diet.
Research Analysis
There are many research studies that have been conducted on thyroid disorders. Here are some key findings from recent studies:
1.Prevalence:
According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, thyroid disorders are more common in women than in men, and the prevalence increases with age. The study found that approximately 12% of women and 3% of men in the United States have thyroid disorders.
2.Environmental factors:
Several studies have investigated the link between environmental factors and thyroid disorders. One study published in Environmental Health Perspectives found that exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals, such as bisphenol A (BPA), may increase the risk of thyroid disorders.
3.Genetic factors:
Genetics also play a role in the development of thyroid disorders. According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, certain genetic variations may increase the risk of thyroid disorders, especially in people with a family history of the condition.
4.Treatment effectiveness:
A study published in Thyroid found that levothyroxine, the medication used to treat hypothyroidism, was effective in normalizing thyroid function in most patients. The study also found that regular monitoring of thyroid function is important to ensure that treatment is effective.
5.Comorbidities:
Thyroid disorders are often associated with other health conditions.
According to a research in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease are more common in patients with hypothyroidism.
These research findings can help healthcare providers better understand the causes and treatment, and can also help inform public health policies aimed at reducing the prevalence of these conditions.
Women’s Demographic
Thyroid disorders are more prevalent in women than men, with women being five to eight times more likely to develop these conditions. This gender disparity is thought to be due to the influence of female hormones on the thyroid gland, as well as the effects of pregnancy and menopause.
According to data from the American Thyroid Association, up to 20% of women will develop such disorder at some point in their lives, compared to 10% of men. Women are also more likely to develop autoimmune thyroid disorders, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease.
The incidence of thyroid disorders in women increases with age, with the highest prevalence seen in women over 60 years old. Pregnancy and postpartum period are also associated with an increased risk of thyroid disorders, particularly thyroiditis. Women with a family history of thyroid disorders are also at higher risk.
Overall, the demographic graph of thyroid disorders in women shows a higher prevalence in this population compared to men, with an increased incidence in older women and those with certain risk factors. It is important for women to be aware of their risk for thyroid disorders and to seek medical attention if they experience symptoms or have a family history of these conditions.
Concluding Thoughts
In conclusion, thyroid disorders are a common health concern, particularly among women and older adults. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for effective management of the condition. While medication is the standard treatment for thyroid disorders, natural remedies may also be helpful in managing symptoms and improving overall thyroid function.
As discussed in the Wellness Kraft article, there are several lifestyle changes and natural remedies that may help improve thyroid health, including reducing stress, getting enough sleep, eating a balanced diet, and taking certain supplements. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before trying any new treatment options.
Research studies have also shed light on the environmental and genetic factors that may contribute to the development of thyroid disorders, as well as the comorbidities associated with these conditions. By understanding the underlying factors that contribute to thyroid disorders, healthcare providers can better diagnose and treat patients with this condition.
Overall, awareness and education about thyroid disorders are crucial for improving public health outcomes and reducing the burden of this condition. With proper management and care, people with thyroid disorders can live healthy and fulfilling lives.
Key Takeaways
1.Thyroid disorders are common among women and older adults, and can have a significant impact on overall health and well-being.
2.Symptoms can vary widely, and may include fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, and more.
3.Accurate diagnosis and management of thyroid disorders requires a thorough medical evaluation, including blood tests and imaging studies.
4.While medication is the standard treatment for thyroid disorders, natural remedies and lifestyle changes may also be helpful in managing symptoms and improving overall thyroid function.
5.Understanding the underlying factors that contribute to thyroid disorders, such as environmental and genetic factors, can help healthcare providers better diagnose and treat patients with this condition.
6.Education and awareness about thyroid disorders are crucial for improving public health outcomes and reducing the burden of this condition.
By staying informed and working closely with healthcare providers, people with thyroid disorders can take steps to manage their condition and improve their quality of life.
FAQs:
1.What is the function of the thyroid gland?
The thyroid gland is a neck-based, butterfly-shaped gland. It creates hormones essential for growth and development and for controlling metabolism.
2.What are the common types of thyroid disorders?
The most common types of thyroid disorders are hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and thyroid nodules.
3.Who is at risk for developing thyroid disorders?
Women, older adults, and individuals with a family history of thyroid disorders are at increased risk.
4.What are the symptoms of thyroid disorders?
Symptoms can vary depending on the type of thyroid disorder, but may include fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, hair loss, and more.
5.How are thyroid disorders diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical exam, blood tests, and imaging studies such as a thyroid ultrasound or biopsy.
6.What are the treatment options for thyroid disorders?
Treatment options may include medication, surgery, or radioactive iodine therapy, depending on the type and severity of the it.
7.Are there natural remedies that can help with thyroid disorders?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as reducing stress, eating a balanced diet, and taking certain supplements may be helpful in managing symptoms and improving thyroid function.
8.Can thyroid disorders be prevented?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent it, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and avoiding exposure to environmental toxins may help reduce the risk.
9.Are there any complications associated with thyroid disorders?
If untreated can lead to a range of complications, including heart problems, osteoporosis, and more.
10.Is it possible to live a healthy life with a thyroid disorder?
Yes, with proper management and care, people can live healthy and fulfilling lives. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan.