“Urinary tract infections are a reminder that our bodies need to be treated with care and respect. Listen to your body, and take action when something doesn’t feel right.” – Wellness Kraft
Introduction
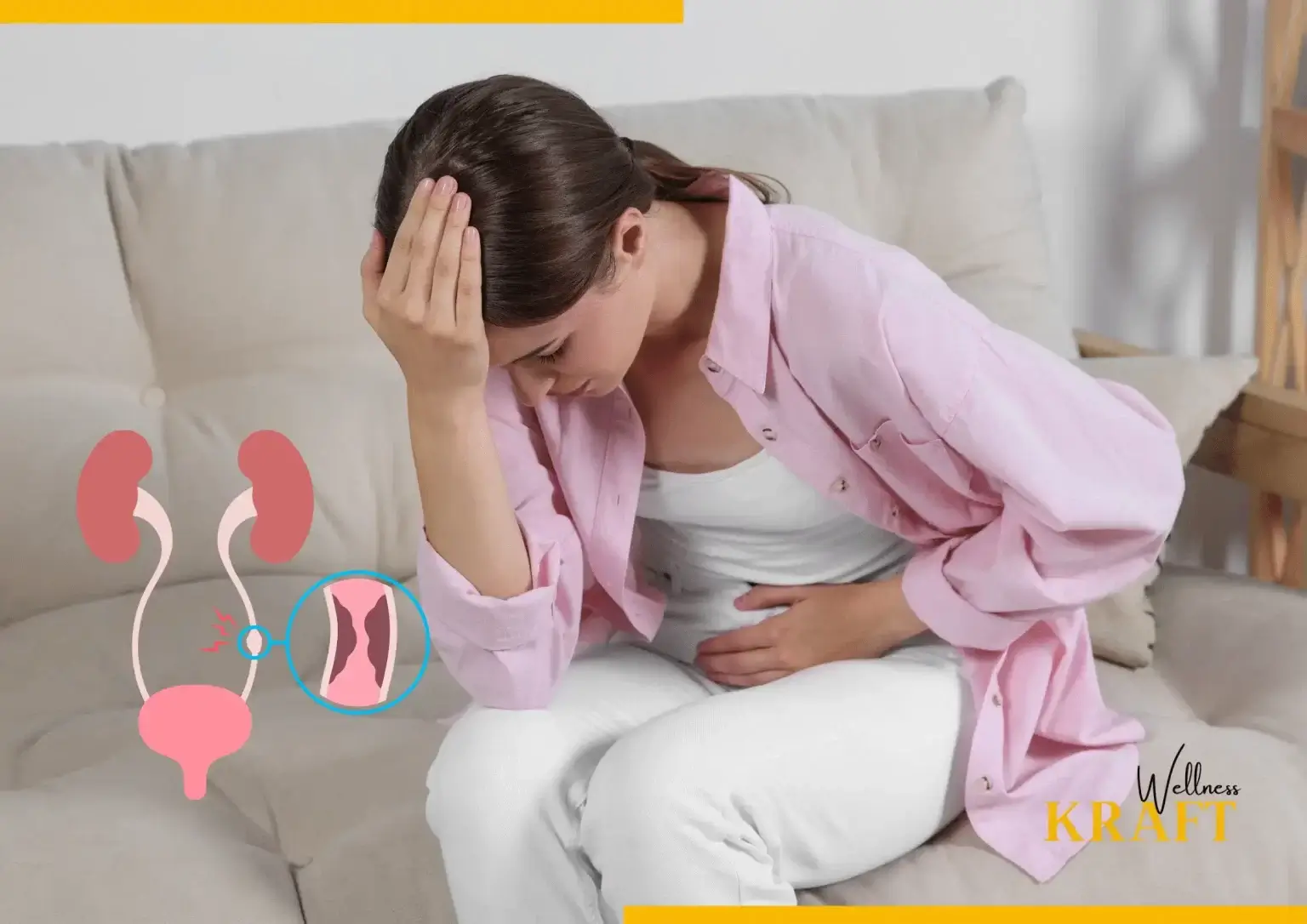
The urinary system, which comprises the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra, is frequently afflicted by urinary tract infections (UTIs). UTIs are typically caused by bacteria, and symptoms may include painful urination, frequent urination, and lower abdominal pain.
Preventing and managing UTIs is important for overall health and well-being. Untreated UTIs can lead to more serious complications, such as kidney damage or sepsis. With proper prevention and management strategies, most UTIs can be treated and prevented from recurring. In the following sections, we will explore the causes and risk factors of UTIs, as well as strategies for preventing and managing UTIs.
Table of Contents
Definition of Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are infections that occur in any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. They are caused by the presence of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), that enter the urinary tract and multiply, leading to inflammation and infection.
UTIs can cause a range of symptoms, including pain or burning during urination, frequent urination, lower abdominal pain, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine. They are more common in women than men, and certain factors such as sexual activity, pregnancy, and menopause can increase the risk of developing a UTI. UTIs can usually be treated with antibiotics, and prevention strategies such as good hygiene practices and staying hydrated can help reduce the risk of developing a UTI.
Importance of Preventing and Managing Urinary Tract Infections

Preventing and managing UTIs is important for several reasons. Firstly, UTIs can cause discomfort and pain, including painful urination, lower abdominal pain, and frequent urination, which can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Secondly, if left untreated, UTIs can lead to more serious complications, such as kidney damage, sepsis, and even death in rare cases. UTIs can also be particularly dangerous for pregnant women and people with compromised immune systems.
Proper prevention and management of UTIs involves a combination of good hygiene practices, dietary and lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, medical treatment. These strategies can help reduce the risk of developing a UTI, prevent recurrent UTIs, and minimize the severity of symptoms if an infection does occur. By taking steps to prevent and manage UTIs, individuals can protect their overall health and well-being, and avoid the potential complications and discomfort associated with these infections.
Risk Factors and Causes of Urinary Tract Infection
The primary cause of UTIs is the presence of bacteria in the urinary tract, most commonly Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria. These bacteria can enter the urinary tract through the urethra and can multiply, leading to inflammation and infection.
Several factors can increase the risk of developing UTIs, including:
Gender:
Women are more prone to UTIs due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria to enter the bladder more easily.
Sexual activity:
Sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urethra, increasing the risk of infection.
Menopause:
Hormonal changes during menopause can thin the walls of the urethra, making it more susceptible to infection.
Urinary tract abnormalities:
Abnormalities in the urinary tract, such as a blockage, can increase the risk of UTIs.
Medical conditions:
Certain medical conditions such as diabetes or conditions that weaken the immune system can make individuals more vulnerable to UTIs.
Use of certain products:
Products such as spermicides and certain types of birth control can increase the risk of UTIs.
Catheterization:
The use of a catheter to drain urine from the bladder can increase the risk of developing a UTI.
By understanding the causes and risk factors of UTIs, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk of developing an infection. This can include practicing good hygiene, staying hydrated, and avoiding behaviors that increase the risk of bacterial introduction into the urinary tract.
Bacteria that Cause Urinary Tract Infection
The majority of UTIs are caused by bacteria, with the most common type being Escherichia coli (E. coli). This bacteria is found in the digestive tract and can easily travel to the urethra and bladder. Other types of bacteria that can cause UTIs include:
Klebsiella:
This type of bacteria can cause a range of infections, including UTIs.
Proteus:
This bacteria is commonly found in the intestines and can cause UTIs in people with underlying medical conditions.
Pseudomonas:
This bacteria is typically found in hospitals and can cause UTIs in people with weakened immune systems or those who have had catheters.
Enterococcus:
This bacteria is typically found in the gastrointestinal tract and can cause UTIs in people with underlying medical conditions.
Staphylococcus:
This bacteria is commonly found on the skin and can cause UTIs in people who have had recent surgery or who have weakened immune systems.
It’s important to note that not all UTIs are caused by bacteria. In some cases, UTIs can be caused by other factors such as yeast infections or sexually transmitted infections. Proper diagnosis and treatment by a healthcare professional is key to effectively managing UTIs.
Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infection

Common symptoms of UTIs include:
1.Pain or burning during urination
2.Frequent urge to urinate, but only passing small amounts of urine
3.Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
4.Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen or back
5.Fatigue and generally feeling unwell
Symptoms that may indicate a more severe UTI or a possible kidney infection include:
1.Fever
2.Chills
3.Nausea and vomiting
4.Pain in the side, back, or groin
5.Blood in the urine
It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these more severe symptoms, as a kidney infection can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. In general, if you suspect you may have a UTI, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Preventing Urinary Tract Infection
Preventing UTIs is key to reducing the risk of infection and managing symptoms. Here are some tips for preventing urinary tract infection:
Practice good hygiene:
Wiping from front to back after using the toilet can help prevent the spread of bacteria from the anus to the urethra. Avoiding douches, feminine hygiene sprays, and harsh soaps in the genital area can also help maintain the natural pH balance of the area.
Stay hydrated:
Drinking plenty of water and fluids can help flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
Urinate frequently:
Urinating regularly and fully can help prevent the buildup of bacteria in the bladder.
Avoid irritating products:
Spermicidal products, certain types of lubricants, and other irritants can increase the risk of UTIs in some people.
Dietary changes:
Certain foods and supplements may help prevent UTIs, such as cranberry juice or supplements, probiotics, and vitamin C.
Urinate after sex:
Urinating after sex can help flush out any bacteria that may have entered the urinary tract during sexual activity.
Wear breathable clothing:
Tight-fitting clothing, especially in the genital area, can create a warm and moist environment that promotes bacterial growth. Opt for breathable fabrics like cotton to keep the area dry and cool.
It’s important to note that while these preventative measures may reduce the risk of UTIs, they may not always be effective. If you suspect you have a UTI, it’s important to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Treating Urinary Tract Infection
Treating UTIs typically involves a course of antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection. The type of antibiotic prescribed will depend on the severity of the infection and the type of bacteria causing it. It’s important to finish the entire course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished, to ensure that the infection is fully treated and to prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
In addition to antibiotics, healthcare providers may recommend pain relief medication to help manage discomfort associated with UTI symptoms. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be effective for mild to moderate pain.
If a person experiences frequent UTIs or recurrent infections, healthcare providers may recommend additional testing to identify underlying causes or contributing factors. For example, an individual with a structural abnormality of the urinary tract may require surgery to correct the issue and reduce the risk of future infections.
Overall, seeking prompt medical attention and completing the full course of antibiotics prescribed is essential for effective treatment of UTIs and prevention of complications.
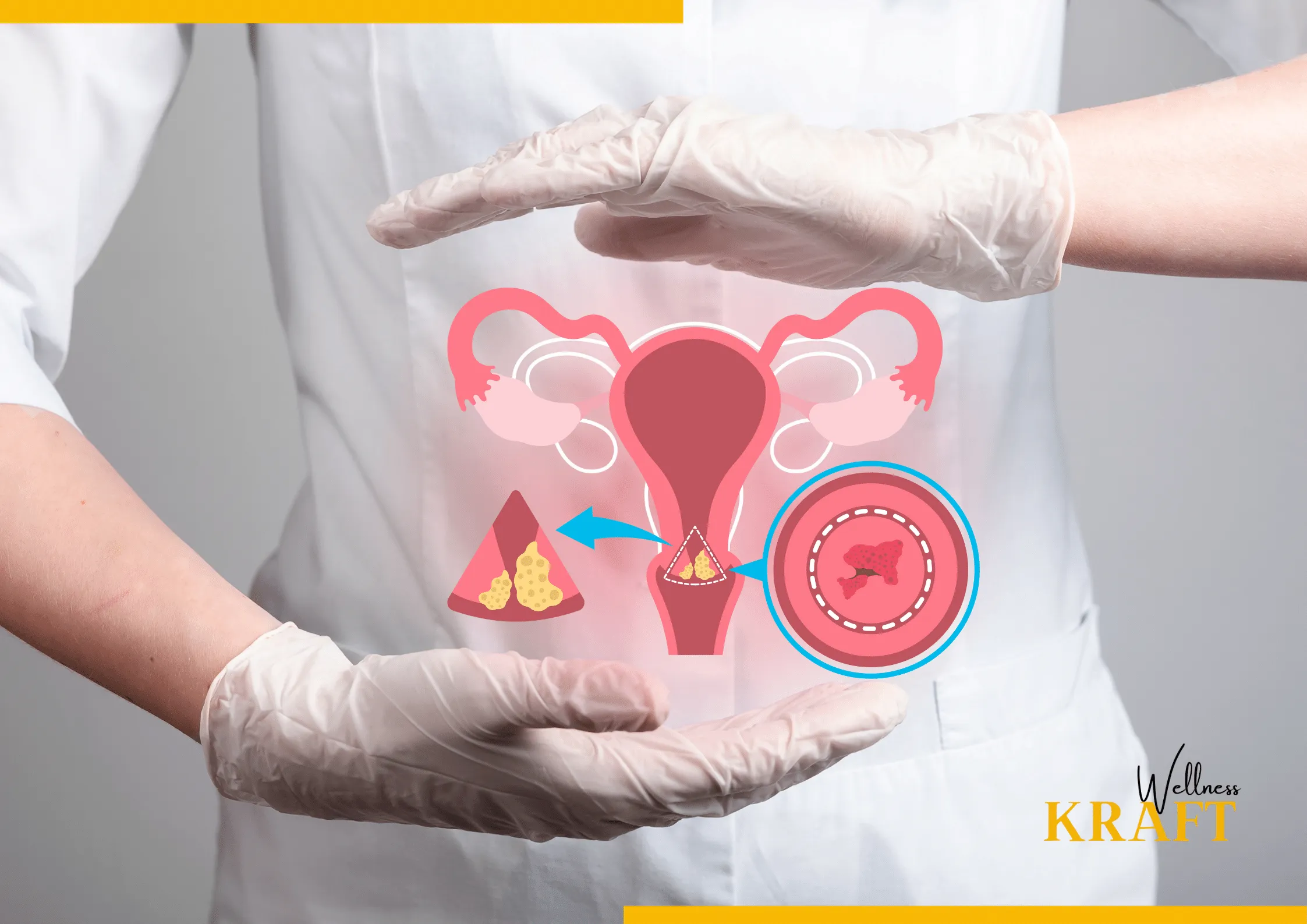
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection
Recurrent urinary tract infection are a common issue for some individuals, especially women. Recurrent UTIs are defined as having three or more UTIs within a 12-month period. There are several factors that may contribute to recurrent UTIs, including:
Bacterial resistance:
Repeated use of antibiotics may lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria that are more difficult to treat.
Underlying health conditions:
Certain underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or kidney stones, may increase the risk of recurrent UTIs.
Structural abnormalities:
Structural abnormalities in the urinary tract, such as a blockage or obstruction, can make it difficult to fully empty the bladder and increase the risk of recurrent infections.
Sexual activity:
Sexual activity can increase the risk of UTIs in some individuals.
Menopause:
Changes in the urinary tract during menopause can make some women more susceptible to UTIs.
If you experience recurrent UTIs, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and develop a personalized treatment plan. Treatment for recurrent UTIs may involve long-term antibiotic therapy, preventative measures, or additional testing to identify any underlying conditions.
Demographic Comparison
Urinary tract infections can affect people of all ages and genders, but there are some differences in the prevalence and risk factors based on demographics. Here is a comparison of UTI prevalence and risk factors based on different demographics:
Gender:
Women are more likely to develop UTIs than men due to having a shorter urethra, which makes it easier for bacteria to enter the bladder. It is estimated that 50-60% of women will experience a UTI in their lifetime, compared to 12% of men.
Age:
UTIs are more common in older adults, especially those over the age of 65. This is due to changes in the urinary tract that occur with aging, as well as a higher prevalence of underlying health conditions that can increase the risk of UTIs.
Pregnancy:
Pregnant women have an increased risk of developing UTIs due to hormonal changes and pressure on the bladder from the growing fetus. UTIs during pregnancy can lead to complications such as preterm labor and low birth weight.
Sexual activity:
Women who are sexually active have a higher risk of developing urinary tract infection, as sexual activity can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract. Using condoms and urinating after sex can help reduce the risk.
Menopause:
Women who have gone through menopause are at an increased risk of UTIs due to changes in the urinary tract that occur with hormonal changes. Hormone replacement therapy may help reduce the risk.
It is important to note that these are general trends and there may be individual differences in UTI risk based on demographics. It is always important to talk to a healthcare provider if you are experiencing symptoms of a UTI or have concerns about your risk factors.
Research Analysis
There is a significant amount of authentic research on urinary tract infections that has been conducted over the years. Some of the notable studies and findings include:
Antibiotic resistance:
Research has shown that the overuse and misuse of antibiotics has led to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria, making it more difficult to treat UTIs. A study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases in 2017 found that the incidence of antibiotic-resistant UTIs had increased significantly over a 10-year period.
Prevention strategies:
Numerous studies have investigated the effectiveness of various prevention strategies for UTIs, such as cranberry supplements, probiotics, and prebiotics. A systematic review published in The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews in 2020 found that cranberry products may reduce the risk of UTIs in some populations.
Underlying health conditions:
Research has also explored the relationship between underlying health conditions, such as diabetes and kidney stones, and the risk of UTIs. A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association in 2019 found that women with diabetes had a higher risk of developing urinary tract infection.
Patient education:
Studies have emphasized the importance of patient education in preventing and managing urinary tract infection. Patient education and followup treatment increased the likelihood of urinary tract infection prevention, according to a 2016 study that was published in the Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine.
Overall, these studies and others have contributed to a better understanding of the causes, risk factors, and prevention and treatment strategies for urinary tract infection.
Concluding Thoughts
In conclusion, urinary tract infections are a common and often painful condition that can have significant health consequences if left untreated. However, there are many effective strategies for preventing and managing urinary tract infection, such as maintaining good hygiene practices, making dietary and lifestyle changes, and seeking prompt medical treatment when necessary.
At Wellness Kraft, we believe in the importance of taking a holistic approach to health and wellness, which includes addressing UTIs and other common conditions through a combination of natural and conventional treatments. By staying informed about the latest research and recommendations for urinary tract infection prevention and management, we can empower ourselves and our community to lead healthier, happier lives.
Key Takeaways
1.Urinary tract infection are a common and often painful condition that can be caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract.
2.Good hygiene practices, such as wiping front to back and urinating after sex, can help prevent UTIs.
3.Dietary and lifestyle changes, such as staying hydrated and avoiding irritants like caffeine and alcohol, may also help prevent UTIs.
4.Prompt medical treatment is important for effectively treating UTIs, which may include antibiotics or other medications.
5.For those who experience recurrent UTIs, additional testing and treatment may be necessary to address underlying issues and prevent future infections.
FAQs
1.What are the most common causes why urinary tract infection occur?
Urinary tract infection are most commonly caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract through the urethra.
2.Can urinary tract infection be prevented?
Yes, urinary tract infection can be prevented through good hygiene practices, dietary and lifestyle changes, and other preventative measures.
3.What are some common symptoms of urinary tract infection?
Common symptoms of urinary tract infection include painful urination, frequent urination, and lower abdominal pain or discomfort.
4.Can antibiotics be used to treat Urinary tract infections?
Yes, antibiotics are often used to effectively treat urinary tract infection.
5.Are there natural remedies for Urinary tract infection?
Some natural remedies, such as cranberry juice or supplements, may help prevent or manage Urinary tract infections, but it is important to speak with a healthcare provider before trying any new treatments.
6.Do women get Urinary tract infection more frequently than men?
Yes, Urinary tract infection are more common in women due to their shorter urethras, which makes it easier for bacteria to enter the urinary tract.
7.Can urinary tract infection lead to more serious health issues?
If left untreated, Urinary tract infections can lead to more serious health issues such as kidney damage or bloodstream infections.
8.Can certain foods or drinks trigger urinary tract infection?
Foods or drinks that irritate the urinary tract, such as caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods, may increase the risk of Urinary tract infections.
9.Can UTIs be sexually transmitted?
While Urinary tract infections are not typically considered sexually transmitted infections, sexual activity can increase the risk of developing a UTI.
10.When should I see a healthcare provider for a UTI?
It is recommended to see a healthcare provider if you experience symptoms of a Urinary tract infection, especially if they are severe or do not improve within a few days.










2 comments